This is a preprint.
Limited impact of Delta variant’s mutations in the effectiveness of neutralization conferred by natural infection or COVID-19 vaccines in a Latino population
- PMID: 34729566
- PMCID: PMC8562550
- DOI: 10.1101/2021.10.25.21265422
Limited impact of Delta variant’s mutations in the effectiveness of neutralization conferred by natural infection or COVID-19 vaccines in a Latino population
Update in
-
Limited Impact of Delta Variant's Mutations on the Effectiveness of Neutralization Conferred by Natural Infection or COVID-19 Vaccines in a Latino Population.Viruses. 2021 Nov 30;13(12):2405. doi: 10.3390/v13122405. Viruses. 2021. PMID: 34960674 Free PMC article.
Abstract
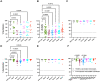
The SARS-CoV-2 pandemic has impacted public health systems all over the world. The Delta variant seems to possess enhanced transmissibility, but no clear evidence suggests it has increased virulence. Our data shows that pre-exposed individuals had similar neutralizing activity against the authentic COVID-19 strain and the Delta and Epsilon variants. After one vaccine dose, the neutralization capacity expands to all tested variants. Healthy vaccinated individuals showed a limited breadth of neutralization. One vaccine dose induced similar neutralizing antibodies against the Delta compared to the authentic strain. However, even after two doses, this capacity only expanded to the Epsilon variant.
Conflict of interest statement
Conflict of Interest
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures
References
-
- Aleem A, Akbar Samad AB, Slenker AK. Emerging Variants of SARS-CoV-2 And Novel Therapeutics Against Coronavirus (COVID-19). StatPearls. Treasure Island (FL): StatPearls Publishing. Copyright © 2021, StatPearls Publishing LLC., 2021. - PubMed
Publication types
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous
