LRG1 is an adipokine that mediates obesity-induced hepatosteatosis and insulin resistance
- PMID: 34730111
- PMCID: PMC8670837
- DOI: 10.1172/JCI148545
LRG1 is an adipokine that mediates obesity-induced hepatosteatosis and insulin resistance
Abstract
Dysregulation in adipokine biosynthesis and function contributes to obesity-induced metabolic diseases. However, the identities and functions of many of the obesity-induced secretory molecules remain unknown. Here, we report the identification of leucine-rich alpha-2-glycoprotein 1 (LRG1) as an obesity-associated adipokine that exacerbates high fat diet-induced hepatosteatosis and insulin resistance. Serum levels of LRG1 were markedly elevated in obese humans and mice compared with their respective controls. LRG1 deficiency in mice greatly alleviated diet-induced hepatosteatosis, obesity, and insulin resistance. Mechanistically, LRG1 bound with high selectivity to the liver and promoted hepatosteatosis by increasing de novo lipogenesis and suppressing fatty acid β-oxidation. LRG1 also inhibited hepatic insulin signaling by downregulating insulin receptor substrates 1 and 2. Our study identified LRG1 as a key molecule that mediates the crosstalk between adipocytes and hepatocytes in diet-induced hepatosteatosis and insulin resistance. Suppressing LRG1 expression and function may be a promising strategy for the treatment of obesity-related metabolic diseases.
Keywords: Diabetes; Endocrinology; Insulin signaling; Metabolism; Obesity.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures
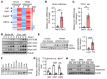
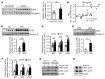
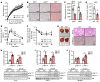
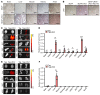

References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous

