An integrative review of nursing leadership in Saudi Arabia
- PMID: 34730295
- PMCID: PMC8685851
- DOI: 10.1002/nop2.1117
An integrative review of nursing leadership in Saudi Arabia
Abstract
Aims: The aims of this integrative review were to describe leadership styles from the nursing literature in Saudi Arabia and to identify the current state of evidence about relationships between leadership styles and nurse, patient and organization outcomes in Saudi Arabia.
Design: Integrative review was used as a design for this study.
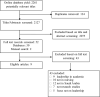
Methods: The following search terms were used with databases: 'Saudi Arabia', 'leadership theory*', 'leadership style*', 'leadership model*', 'management style' and 'nurse*'. Methodological quality was assessed using two different quality rating tools for quantitative and qualitative studies. Databases used for this review included Nursing & Allied Health Database, Cochrane Database of Systematic Reviews, PubMed, CINAHL, Embase, PsycINFO, Scopus, Web of Science and ProQuest Dissertations & Theses.
Results: Nine manuscripts representing eight studies were included in this review. The papers reviewed included quantitative (n = 6), qualitative (n = 2) and mixed methods studies (n = 1). Results were grouped into different themes, identified as nursing leadership styles in Saudi Arabia, leadership styles and nurses' outcomes, and demographics and leadership styles.
Keywords: Saudi Arabia; integrative review; leadership styles; leadership theories; literature review; nursing; review.
© 2021 The Authors. Nursing Open published by John Wiley & Sons Ltd.
Conflict of interest statement
There is no conflict of interest.
All authors contributed to the conception of the study. BA and MK reviewed the included studies and screened them. CW and DW reviewed the result section to make sure about the consistency with the tables. All authors contributed to the interpretation of the results and approved the final version of the study.
References
-
- Aldawood, A. (2017). Developing culturally appropriate leadership for nursing in Saudi Arabia. [Unpublished doctoral dissertation]. Cardiff University.
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources