Temporal dynamics of base excision/single-strand break repair protein complex assembly/disassembly are modulated by the PARP/NAD+/SIRT6 axis
- PMID: 34731617
- PMCID: PMC8607749
- DOI: 10.1016/j.celrep.2021.109917
Temporal dynamics of base excision/single-strand break repair protein complex assembly/disassembly are modulated by the PARP/NAD+/SIRT6 axis
Abstract
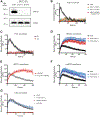
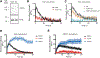
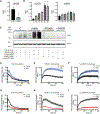
Assembly and disassembly of DNA repair protein complexes at DNA damage sites are essential for maintaining genomic integrity. Investigating factors coordinating assembly of the base excision repair (BER) proteins DNA polymerase β (Polβ) and XRCC1 to DNA lesion sites identifies a role for Polβ in regulating XRCC1 disassembly from DNA repair complexes and, conversely, demonstrates Polβ's dependence on XRCC1 for complex assembly. LivePAR, a genetically encoded probe for live-cell imaging of poly(ADP-ribose) (PAR), reveals that Polβ and XRCC1 require PAR for repair-complex assembly, with PARP1 and PARP2 playing unique roles in complex dynamics. Further, BER complex assembly is modulated by attenuation/augmentation of NAD+ biosynthesis. Finally, SIRT6 does not modulate PARP1 or PARP2 activation but does regulate XRCC1 recruitment, leading to diminished Polβ abundance at sites of DNA damage. These findings highlight coordinated yet independent roles for PARP1, PARP2, and SIRT6 and their regulation by NAD+ bioavailability to facilitate BER.
Keywords: BER; DNA polymerase β; LivePAR; NAD(+); NRH; PAR; SIRT6; SSBR; XRCC1; poly(ADP-ribose).
Copyright © 2021 The Author(s). Published by Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
Conflict of interest statement
Declaration of interests R.W.S. is a scientific consultant for Canal House Biosciences, but this company was not involved in this study, nor was the consulting work related to this study. The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures


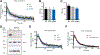

Similar articles
-
Oncometabolite 2-hydroxyglutarate suppresses basal protein levels of DNA polymerase beta that enhances alkylating agent and PARG inhibition induced cytotoxicity.DNA Repair (Amst). 2024 Aug;140:103700. doi: 10.1016/j.dnarep.2024.103700. Epub 2024 Jun 4. DNA Repair (Amst). 2024. PMID: 38897003 Free PMC article.
-
XRCC1 mediates PARP1- and PAR-dependent recruitment of PARP2 to DNA damage sites.Nucleic Acids Res. 2025 Feb 8;53(4):gkaf086. doi: 10.1093/nar/gkaf086. Nucleic Acids Res. 2025. PMID: 39970298 Free PMC article.
-
Quantitative Analysis of Nuclear Poly(ADP-Ribose) Dynamics in Response to Laser-Induced DNA Damage.Methods Mol Biol. 2023;2609:43-59. doi: 10.1007/978-1-0716-2891-1_3. Methods Mol Biol. 2023. PMID: 36515828 Free PMC article.
-
NAD+-mediated regulation of mammalian base excision repair.DNA Repair (Amst). 2020 Sep;93:102930. doi: 10.1016/j.dnarep.2020.102930. DNA Repair (Amst). 2020. PMID: 33087267 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The dynamics and regulation of PARP1 and PARP2 in response to DNA damage and during replication.DNA Repair (Amst). 2024 Aug;140:103690. doi: 10.1016/j.dnarep.2024.103690. Epub 2024 May 25. DNA Repair (Amst). 2024. PMID: 38823186 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
A Double-Edged Sword: The Two Faces of PARylation.Int J Mol Sci. 2022 Aug 29;23(17):9826. doi: 10.3390/ijms23179826. Int J Mol Sci. 2022. PMID: 36077221 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Poly-ADP-ribosylation dynamics, signaling, and analysis.Environ Mol Mutagen. 2024 Nov;65(9):315-337. doi: 10.1002/em.22623. Epub 2024 Sep 2. Environ Mol Mutagen. 2024. PMID: 39221603 Review.
-
Oncometabolite 2-hydroxyglutarate suppresses basal protein levels of DNA polymerase beta that enhances alkylating agent and PARG inhibition induced cytotoxicity.DNA Repair (Amst). 2024 Aug;140:103700. doi: 10.1016/j.dnarep.2024.103700. Epub 2024 Jun 4. DNA Repair (Amst). 2024. PMID: 38897003 Free PMC article.
-
The expanding universe of PARP1-mediated molecular and therapeutic mechanisms.Mol Cell. 2022 Jun 16;82(12):2315-2334. doi: 10.1016/j.molcel.2022.02.021. Epub 2022 Mar 9. Mol Cell. 2022. PMID: 35271815 Free PMC article. Review.
-
TRIP12's role in the governance of DNA polymerase β involvement in DNA damage response and repair.Nucleic Acids Res. 2025 Jun 20;53(12):gkaf574. doi: 10.1093/nar/gkaf574. Nucleic Acids Res. 2025. PMID: 40613707 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Chiarugi A, Dӧlle C, Felici R, and Ziegler M (2012). The NAD metabolome–a key determinant of cancer cell biology. Nat. Rev. Cancer 12, 741–752. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

