FARP1, ARHGEF39, and TIAM2 are essential receptor tyrosine kinase effectors for Rac1-dependent cell motility in human lung adenocarcinoma
- PMID: 34731623
- PMCID: PMC8627373
- DOI: 10.1016/j.celrep.2021.109905
FARP1, ARHGEF39, and TIAM2 are essential receptor tyrosine kinase effectors for Rac1-dependent cell motility in human lung adenocarcinoma
Abstract
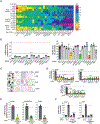
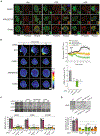
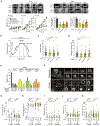
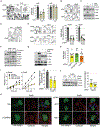
Despite the undisputable role of the small GTPase Rac1 in the regulation of actin cytoskeleton reorganization, the Rac guanine-nucleotide exchange factors (Rac-GEFs) involved in Rac1-mediated motility and invasion in human lung adenocarcinoma cells remain largely unknown. Here, we identify FARP1, ARHGEF39, and TIAM2 as essential Rac-GEFs responsible for Rac1-mediated lung cancer cell migration upon EGFR and c-Met activation. Noteworthily, these Rac-GEFs operate in a non-redundant manner by controlling distinctive aspects of ruffle dynamics formation. Mechanistic analysis reveals a leading role of the AXL-Gab1-PI3K axis in conferring pro-motility traits downstream of EGFR. Along with the positive association between the overexpression of Rac-GEFs and poor lung adenocarcinoma patient survival, we show that FARP1 and ARHGEF39 are upregulated in EpCam+ cells sorted from primary human lung adenocarcinomas. Overall, our study reveals fundamental insights into the complex intricacies underlying Rac-GEF-mediated cancer cell motility signaling, hence underscoring promising targets for metastatic lung cancer therapy.
Keywords: ARHGEF39; AXL; EGFR; FARP1; Rac-GEF; Rac1; TIAM2; lung cancer; migration; ruffles.
Copyright © 2021 The Author(s). Published by Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
Conflict of interest statement
Declaration of interests The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures


References
-
- Abella JV, Vaillancourt R, Frigault MM, Ponzo MG, Zuo D, Sangwan V, Larose L, and Park M (2010). The Gab1 scaffold regulates RTK-dependent dorsal ruffle formation through the adaptor Nck. J. Cell Sci 123, 1306–1319. - PubMed
-
- Bagci H, Sriskandarajah N, Robert A, Boulais J, Elkholi IE, Tran V, Lin ZY, Thibault MP, Dubé N, Faubert D, et al. (2020). Mapping the proximity interaction network of the Rho-family GTPases reveals signalling pathways and regulatory mechanisms. Nat. Cell Biol 22, 120–134. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

