An airway organoid-based screen identifies a role for the HIF1α-glycolysis axis in SARS-CoV-2 infection
- PMID: 34731648
- PMCID: PMC8516798
- DOI: 10.1016/j.celrep.2021.109920
An airway organoid-based screen identifies a role for the HIF1α-glycolysis axis in SARS-CoV-2 infection
Abstract
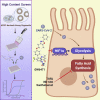
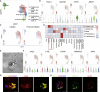
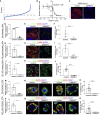
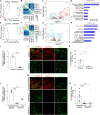
It is urgent to develop disease models to dissect mechanisms regulating severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2 (SARS-CoV-2) infection. Here, we derive airway organoids from human pluripotent stem cells (hPSC-AOs). The hPSC-AOs, particularly ciliated-like cells, are permissive to SARS-CoV-2 infection. Using this platform, we perform a high content screen and identify GW6471, which blocks SARS-CoV-2 infection. GW6471 can also block infection of the B.1.351 SARS-CoV-2 variant. RNA sequencing (RNA-seq) analysis suggests that GW6471 blocks SARS-CoV-2 infection at least in part by inhibiting hypoxia inducible factor 1 subunit alpha (HIF1α), which is further validated by chemical inhibitor and genetic perturbation targeting HIF1α. Metabolic profiling identifies decreased rates of glycolysis upon GW6471 treatment, consistent with transcriptome profiling. Finally, xanthohumol, 5-(tetradecyloxy)-2-furoic acid, and ND-646, three compounds that suppress fatty acid biosynthesis, also block SARS-CoV-2 infection. Together, a high content screen coupled with transcriptome and metabolic profiling reveals a key role of the HIF1α-glycolysis axis in mediating SARS-CoV-2 infection of human airway epithelium.
Keywords: GW4671; SARS-CoV-2; airway organoid; fatty acid synthesis; high content drug screen; hypoxia-inducible factor 1-alpha.
Copyright © 2021 The Author(s). Published by Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
Conflict of interest statement
Declaration of interests R.E.S. is on the scientific advisory board of Miromatrix. T.R.E. and S.C. are the co-founders of OncoBeat.
Figures



Comment in
-
Comments on 'An airway organoid-based screen identifies a role for the HIF1α‒glycolysis axis in SARS-CoV-2 infection'.J Mol Cell Biol. 2022 Feb 24;14(1):mjab075. doi: 10.1093/jmcb/mjab075. J Mol Cell Biol. 2022. PMID: 34850919 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
References
-
- Appelberg S., Gupta S., Svensson Akusjärvi S., Ambikan A.T., Mikaeloff F., Saccon E., Végvári Á., Benfeitas R., Sperk M., Ståhlberg M., et al. Dysregulation in Akt/mTOR/HIF-1 signaling identified by proteo-transcriptomics of SARS-CoV-2 infected cells. Emerg. Microbes Infect. 2020;9:1748–1760. - PMC - PubMed
-
- Bakhache W., Neyret A., McKellar J., Clop C., Bernard E., Weger-Lucarelli J., Briant L. Fatty acid synthase and stearoyl-CoA desaturase-1 are conserved druggable cofactors of Old World Alphavirus genome replication. Antiviral Res. 2019;172:104642. - PubMed
-
- Berenguer J., Ryan P., Rodríguez-Baño J., Jarrín I., Carratalà J., Pachón J., Yllescas M., Arriba J.R., Muñoz E.A., Divasson P.G., et al. Characteristics and predictors of death among 4035 consecutively hospitalized patients with COVID-19 in Spain. Clin. Microbiol. Infect. 2020;26:1525–1536. - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Supplementary concepts
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

