The Therapeutic Evaluation of Steroids in IgA Nephropathy Global (TESTING) Study: Trial Design and Baseline Characteristics
- PMID: 34731857
- PMCID: PMC8744003
- DOI: 10.1159/000519812
The Therapeutic Evaluation of Steroids in IgA Nephropathy Global (TESTING) Study: Trial Design and Baseline Characteristics
Abstract
Introduction: Despite optimal current care, up to 30% of individuals suffering from immunoglobulin A nephropathy (IgAN) will develop kidney failure requiring dialysis or kidney transplantation. The Therapeutic Evaluation of STeroids in IgA Nephropathy Global (TESTING) study was designed to assess the benefits and risks of steroids in people with IgAN. We report the trial design as well as the baseline characteristics of study participants.
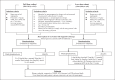
Methods: It is an investigator-initiated, multicenter, double-blind, placebo-controlled, randomized trial of individuals with kidney biopsy-confirmed IgAN, proteinuria ≥1 g/day, and an estimated GFR of 20-120 mL/min/1.73 m2, following at least 3 months of standard of care including maximum labelled (or tolerated) dose of renin-angiotensin system blockade. The original study design randomized participants 1:1 to oral methylprednisolone (0.6-0.8 mg/kg/day, maximum 48 mg/day) for 2 months, with subsequent weaning by 8 mg/day/month over 6-8 months, or matching placebo. The intervention was modified in 2016 (due to an excess of serious infection) to low-dose methylprednisolone (0.4 mg/kg/day, maximum 32 mg/day) for 2 months, followed by weaning by 4 mg/day/month over 6-9 months, or matching placebo. Participants recruited after 2016 also received prophylaxis against Pneumocystis jirovecii pneumonia during the first 12 weeks of treatment.
Results: The study recruitment period extended from May 2012 to November 2019. By the time the excess of serious infections was observed, 262 participants had been randomized to the original full-dose treatment algorithm, and an interim analysis was reported in 2016. Subsequently, 241 additional participants were randomized to a revised low-dose protocol, for a total of 503 participants from China (373), India (78), Canada (24), Australia (18), and Malaysia (10). The mean age of randomized participants was 38, 39% were female, mean eGFR at randomization was 62.7 mL/min/1.73 m2, and mean 24-h urine protein 2.54 g. The primary endpoint is a composite of 40% eGFR decline from baseline or kidney failure (dialysis, transplantation, or death due to kidney disease), and participants will be followed until the primary outcome has been observed in at least 160 randomized participants. Analyses will also be made across predefined subgroups. Effects on eGFR slope and albuminuria will also be assessed overall, as well as by the steroid dosing regimen.
Conclusions: The TESTING study (combined full and low dose) will define the benefits of corticosteroid use on major kidney outcomes, as well as the risks of therapy, and provide data on the relative effects of different doses, in individuals with high-risk IgAN.
Keywords: Glucocorticoids; IgA nephropathy; Kidney failure.
© 2021 The Author(s). Published by S. Karger AG, Basel.
Conflict of interest statement
Muh Geot Wong has received fees for advisory boards, steering committee roles, or scientific presentations from Travere, Baxter, Amgen, Abbvie, Chinook, Dimerix, Otsuka, GlaxoSmithKline, and CSL-Behring. JiChing Lv has received consultation fees from Chinook therapeutics and KBP Biosciences. Michelle A. Hladunewich has received research funding from Chemocentryx, Ionis, Calliditas Therapeutics, Pfizer, and Roche and consultation fees from Alnylam Pharmaceuticals. Vivekanand Jha has received research grants and honoraria for consultancy and advisory board from Baxter, GSK, and AstraZeneca. Minghui Zhao has received consultation fees from Novartis, Roche, AstraZeneca, and GlaxoSmithKline. David Johnson has received consultancy fees, research grants, speaker's honoraria, and travel sponsorships from Baxter Healthcare and Fresenius Medical Care, consultancy fees from AstraZeneca, Bayer, and AWAK, speaker's honoraria from Ono and Boehringer Ingelheim and Lilly, and travel sponsorships from Ono and Amgen. David Johnson is the current recipient of an Australian National Health and Medical Research Council (NHMRC) Leadership Investigator Grant. Laurent Billot has received speaker's honoraria from Novo Nordisk. Heather Reich has received consultation honoraria from Calliditas, Chinook, Omeros, Alnylam, Retrophin, and Norvartis. Meg J. Jardine is supported by a Medical Research Future Fund Next Generation Clinical Researchers Program Career Development Fellowship; is responsible for research projects that have received unrestricted funding from Amgen, Baxter, CSL, Eli Lilly, Gambro, and MSD; has served on advisory boards sponsored by Akebia, AstraZeneca, Baxter, Bayer, Boehringer Ingelheim, MSD, and Vifor; serves/has served on Steering Committee for trials sponsored by Chinook, CSL, and Janssen; serves on a Steering Committee for an investigator-initiated trial with funding support from Dimerix; spoken at scientific meetings sponsored by Amgen, Janssen, Merck, Roche, and Vifor, with any consultancy, honoraria, or travel support paid to her institution. Mark Woodward has received consultation fees from Amgen, Kyowa Kirin, and Freeline. David C. Wheeler has received honoraria and/or speaker fees from AstraZeneca, Astellas, Amgen, Bayer, Boehringer Ingelheim, GlaxoSmithKline, Janssen, Napp, Mundipharma, Merck Sharp and Dohme, Tricia, Vifor, and Zydus. Richard Glassock has received consultation fees from Chemocentryx, Omeros, Ionis, Travere, Horizon, BioCryst, Equillium, Calliditas, RenaSight (Natera), Novartis, Otsuka, and UpTo Date (Wolters Kluwer Health). Alan Cass was a recipient of the Australian NHMRC Project Grant for the current study and a current recipient of a NHMRC Leadership Investigator Grant. Jürgen Floege has received consultation honoraria from Abgenix, Calliditas, Idorsia, Novartis, Omeros, Travere, and Visterra. Giuseppe Remuzzi has received consultation fees from BioCryst Pharmaceuticals, Inc., and Menarini Ricerche Spa. Yangfeng Wu has received consultation fees from the World Health Organization, China Office, for the hypertension and noncommunicable disease program. Rajiv Agarwal has received consultation fees from Akebia, Boehringer, Bayer, Chinook, Diamedica, Reata, Vifor, and Vertex. Hong Zhang has received consultation fees and serves in the Steering Committee for Janssen, Novartis. Omeros, Calliditas, and Chinook. Vlado Perkovic has received fees for advisory boards, steering committee roles, or scientific presentations from AbbVie, Astellas, AstraZeneca, Bayer, Baxter, Bristol-Myers Squibb, Boehringer Ingelheim, Chinook, Dimerix, Durect, Eli Lilly, Gilead, GlaxoSmithKline, Janssen, Merck, Mitsubishi Tanabe, Mundipharma, Novartis, Novo Nordisk, Pfizer, PharmaLink, Relypsa, Sanofi, Servier, Travere, Vifor, and Tricida.
Figures
References
-
- D'Amico G. The commonest glomerulonephritis in the world: IgA nephropathy. Q J Med. 1987;64((245)):709–27. - PubMed
-
- Schena FP, Pesce F. Chapter 2: epidemiology and ancestral difference. Singapore World Scientific; 2009. Epidemiology and ancestral difference; pp. p. 9–19.
-
- Donadio JV, Bergstralh EJ, Grande JP, Rademcher DM. Proteinuria patterns and their association with subsequent end-stage renal disease in IgA nephropathy. Nephrol Dial Transplant. 2002;17((10)):1197–203. - PubMed
-
- Reich HN, Troyanov S, Scholey JW, Cattran DC, for the Toronto Glomerulonephritis Registry Remission of proteinuria improves prognosis in IgA nephropathy. J Am Soc Nephrol. 2007;18((12)):3177–83. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous