Interplay Between Skin Microbiota Dysbiosis and the Host Immune System in Psoriasis: Potential Pathogenesis
- PMID: 34733291
- PMCID: PMC8558530
- DOI: 10.3389/fimmu.2021.764384
Interplay Between Skin Microbiota Dysbiosis and the Host Immune System in Psoriasis: Potential Pathogenesis
Abstract
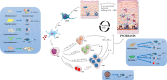
Psoriasis is a multifactorial immune-mediated disease. The highly effective and eligible treatment for psoriasis is limited, for its specific pathogenesis is incompletely elucidated. Skin microbiota is a research hotspot in the pathogenesis of immune-mediated inflammatory skin diseases nowadays, and it may have significant involvement in the provocation or exacerbation of psoriasis with broadly applicable prospects. It is postulated that skin microbiota alternation may interplay with innate immunity such as antimicrobial peptides and Toll-like receptors to stimulate T-cell populations, resulting in immune cascade responses and ultimately psoriasis. Achieving a thorough understanding of its underlying pathogenesis is crucial. Herein, we discuss the potential immunopathogenesis of psoriasis from the aspect of skin microbiota in an attempt to yield insights for novel therapeutic and preventive modalities for psoriasis.
Keywords: Th17; immunology; inflammation; pathogenesis; psoriasis; skin microbiota.
Copyright © 2021 Liang, Ou, Zhuang, Li, Zhang, Zhong and Chen.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

