Effect of Epidemic Intermittent Fasting on Cardiometabolic Risk Factors: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis of Randomized Controlled Trials
- PMID: 34733872
- PMCID: PMC8558421
- DOI: 10.3389/fnut.2021.669325
Effect of Epidemic Intermittent Fasting on Cardiometabolic Risk Factors: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis of Randomized Controlled Trials
Abstract
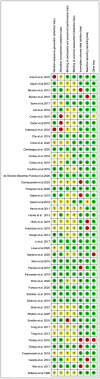
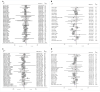
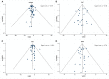
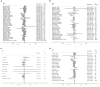
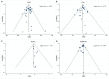
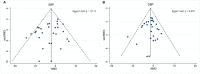
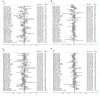
Intermittent fasting (IF) has gained attention as a promising diet for weight loss and dysmetabolic diseases management. This systematic review aimed to investigate the effects of IF on cardiometabolic risk factors (CMRFs). A systematic literature search was carried out using three electronic databases, namely PubMed, Embase, and the Cochrane Library, until October 2020. Randomized controlled trials that compared the IF intervention with a control group diet were included. Fourteen effect sizes were expressed as weighted mean difference (WMD) using a fixed-effects model and 95% confidence intervals (CI). Compared to the ones within control groups, participants exposed to the IF intervention reduced their body weight (WMD, -1.78 kg; 95% CI, -2.21 to -1.35; p <0.05), waist circumference (WMD, -1.19 cm; 95% CI, -1.8 to -0.57; p <0.05), fat mass (WMD, -1.26 kg; 95% CI, -1.57 to -0.95; p <0.05), body mass index (WMD, -0.58 kg/m2; 95% CI, -0.8 to -0.37; p <0.05), systolic blood pressure (WMD, -2.14 mmHg; 95% CI: -3.54 to -0.73; p <0.05), diastolic blood pressure (WMD: -1.38 mmHg, 95% CI, -2.35 to -0.41, p <0.05), fasting blood glucose (WMD: -0.053 mmol/L; 95% CI: -0.105 to 0.001; p <0.05), fasting insulin (WMD, -0.8 mIU/L; 95% CI, -1.15 to -0.44; p <0.05), insulin resistance (WMD, -0.21; 95% CI, -0.36 to -0.05; p <0.05), total cholesterol (WMD, -0.10 mmol/L; 95% CI, -0.17 to -0.02; p <0.05), and triglycerides (WMD, -0.09 mmol/L; 95% CI, -0.13 to -0.04; p <0.05). No effects were observed for low-density lipoprotein cholesterol, high-density lipoprotein cholesterol, or glycosylated hemoglobin. This meta-analysis supports the role of IF in improving the component composition of CMRFs, including weight, waist circumference, fat mass, BMI, blood pressure, total cholesterol, triglycerides, fasting insulin, and insulin resistance, compared to a control group diet. Further research on IF interventions should take into account long-term and well-designed administration to draw definitive conclusions.
Keywords: blood lipid; blood pressure; cardiometabolic risk factors; fasting blood glucose; intermittent fasting; meta-analysis; weight loss.
Copyright © 2021 Yang, Liu, Liu, Pan, Li, Tian, Sun, Yang, Zhao, An, Yang, Gao and Xing.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
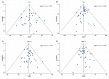
Figures

References
-
- Nichols GA, Horberg M, Koebnick C, Young DR, Waitzfelder B, Sherwood NE, et al. Cardiometabolic risk factors among 1.3 million adults with overweight or obesity, but not diabetes, in 10 geographically diverse regions of the United States, 2012-2013. Prev Chronic Dis. (2017) 14:E22. 10.5888/pcd14.160438 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Danaei G, Lu Y, Singh GM, Carnahan E, Stevens GA, Cowan MJ, et al. Cardiovascular disease, chronic kidney disease, and diabetes mortality burden of cardiometabolic risk factors from 1980 to 2010: a comparative risk assessment. Lancet Diabetes Endocrinol. (2014) 2:634–47. 10.1016/S2213-8587(14)70102-0 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

