HI-NESS: a family of genetically encoded DNA labels based on a bacterial nucleoid-associated protein
- PMID: 34734265
- PMCID: PMC8789088
- DOI: 10.1093/nar/gkab993
HI-NESS: a family of genetically encoded DNA labels based on a bacterial nucleoid-associated protein
Abstract
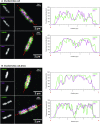
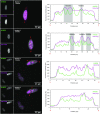
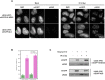
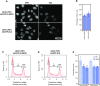
The interplay between three-dimensional chromosome organisation and genomic processes such as replication and transcription necessitates in vivo studies of chromosome dynamics. Fluorescent organic dyes are often used for chromosome labelling in vivo. The mode of binding of these dyes to DNA cause its distortion, elongation, and partial unwinding. The structural changes induce DNA damage and interfere with the binding dynamics of chromatin-associated proteins, consequently perturbing gene expression, genome replication, and cell cycle progression. We have developed a minimally-perturbing, genetically encoded fluorescent DNA label consisting of a (photo-switchable) fluorescent protein fused to the DNA-binding domain of H-NS - a bacterial nucleoid-associated protein. We show that this DNA label, abbreviated as HI-NESS (H-NS-based indicator for nucleic acid stainings), is minimally-perturbing to genomic processes and labels chromosomes in eukaryotic cells in culture, and in zebrafish embryos with preferential binding to AT-rich chromatin.
© The Author(s) 2021. Published by Oxford University Press on behalf of Nucleic Acids Research.
Figures





References
-
- Dame R.T., Rashid F.Z.M., Grainger D.C.. Chromosome organization in bacteria: mechanistic insights into genome structure and function. Nat. Rev. Genet. 2020; 21:227–242. - PubMed
-
- Dame R.T., Tark-Dame M.. Bacterial chromatin: converging views at different scales. Curr. Opin. Cell Biol. 2016; 40:60–65. - PubMed
-
- Banerjee D., Pal S.K.. Dynamics in the DNA recognition by DAPI: exploration of the various binding modes. J. Phys. Chem. B. 2008; 112:1016–1021. - PubMed
-
- Trotta E., D’Ambrosio E., Ravagnan G., Paci M. Simultaneous and different binding mechanisms of 4′,6-diamidino-2-phenylindole to DNA hexamer (d(CGATCG))2: A 1H NMR study. J. Biol. Chem. 1996; 271:27608–27614. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

