Coronary computed tomography angiography in children
- PMID: 34734316
- PMCID: PMC8566193
- DOI: 10.1007/s00247-021-05209-2
Coronary computed tomography angiography in children
Abstract
Imaging the coronary arteries of children, with their faster heart rates, small vessel size and common inability to lie still or breath-hold, has been a major challenge. With numerous advances in technology, CT examinations can now be performed quickly, often with children free-breathing and with much lower radiation doses than previously. This has led to increased use in children. Care must be taken with technique and choice of electrocardiogram (ECG)-gating technique to obtain adequate imaging for a diagnosis while keeping radiation dose as low as reasonably achievable (ALARA). In this paper, we discuss techniques and tips for CT imaging of the coronary arteries in children, including use of dual-source- and ultrawide-detector CT scanners.
Keywords: Anomaly; Children; Computed tomography; Congenital heart disease; Coronary arteries; Dual-source computed tomography; Heart.
© 2021. The Author(s), under exclusive licence to Springer-Verlag GmbH Germany, part of Springer Nature.
Conflict of interest statement
None
Figures


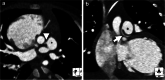
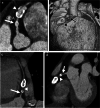
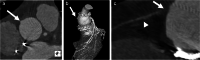


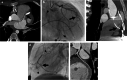
References
-
- Frommelt P, Lopez L, Dimas VV, et al. Recommendations for multimodality assessment of congenital coronary anomalies: a guide from the American Society of Echocardiography: developed in collaboration with the Society for Cardiovascular Angiography and Interventions, Japanese Society of Echocardiography, and Society for Cardiovascular Magnetic Resonance. J Am Soc Echocardiogr. 2020;33:259–294. doi: 10.1016/j.echo.2019.10.011. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Han BK, Rigsby CK, Leipsic J, et al. Computed tomography imaging in patients with congenital heart disease, part 2: technical recommendations. An expert consensus document of the Society of Cardiovascular Computed Tomography (SCCT): endorsed by the Society of [sic] Pediatric Radiology (SPR) and the North American Society of Cardiac Imaging (NASCI) J Cardiovasc Comput Tomogr. 2015;9:493–513. doi: 10.1016/j.jcct.2015.07.007. - DOI - PubMed

