Sympathetic nerve-adipocyte interactions in response to acute stress
- PMID: 34735579
- PMCID: PMC8567732
- DOI: 10.1007/s00109-021-02157-0
Sympathetic nerve-adipocyte interactions in response to acute stress
Abstract
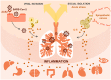
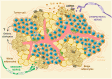
Psychological stress predisposes our body to several disorders. Understanding the cellular and molecular mechanisms involved in the physiological responses to psychological stress is essential for the success of therapeutic applications. New studies show, by using in vivo inducible Cre/loxP-mediated approaches in combination with pharmacological blockage, that sympathetic nerves, activated by psychological stress, induce brown adipocytes to produce IL-6. Strikingly, this cytokine promotes gluconeogenesis in hepatocytes, that results in the decline of tolerance to inflammatory organ damage. The comprehension arising from this research will be crucial for the handling of many inflammatory diseases. Here, we review recent advances in our comprehension of the sympathetic nerve-adipocyte axis in the tissue microenvironment.
Keywords: Adipocytes; Hepatocytes; IL-6; Microenvironment; Sympathetic nerves.
© 2021. The Author(s), under exclusive licence to Springer-Verlag GmbH Germany, part of Springer Nature.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures


References
-
- Rodrigues ACZ, Messi ML, Wang ZM, Abba MC, Pereyra A, Birbrair A, Zhang T, O’Meara M, Kwan P, Lopez EIS, et al. The sympathetic nervous system regulates skeletal muscle motor innervation and acetylcholine receptor stability. Acta Physiol (Oxf) 2019;225:e13195. doi: 10.1111/apha.13195. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

