Chromatin-accessibility estimation from single-cell ATAC-seq data with scOpen
- PMID: 34737275
- PMCID: PMC8568974
- DOI: 10.1038/s41467-021-26530-2
Chromatin-accessibility estimation from single-cell ATAC-seq data with scOpen
Abstract
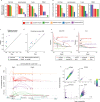
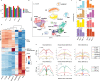
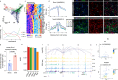
A major drawback of single-cell ATAC-seq (scATAC-seq) is its sparsity, i.e., open chromatin regions with no reads due to loss of DNA material during the scATAC-seq protocol. Here, we propose scOpen, a computational method based on regularized non-negative matrix factorization for imputing and quantifying the open chromatin status of regulatory regions from sparse scATAC-seq experiments. We show that scOpen improves crucial downstream analysis steps of scATAC-seq data as clustering, visualization, cis-regulatory DNA interactions, and delineation of regulatory features. We demonstrate the power of scOpen to dissect regulatory changes in the development of fibrosis in the kidney. This identifies a role of Runx1 and target genes by promoting fibroblast to myofibroblast differentiation driving kidney fibrosis.
© 2021. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures

References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials

