A Brainstem reticulotegmental neural ensemble drives acoustic startle reflexes
- PMID: 34737329
- PMCID: PMC8568936
- DOI: 10.1038/s41467-021-26723-9
A Brainstem reticulotegmental neural ensemble drives acoustic startle reflexes
Abstract
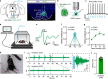
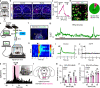
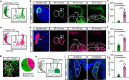
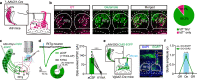
The reticulotegmental nucleus (RtTg) has long been recognized as a crucial component of brainstem reticular formation (RF). However, the function of RtTg and its related circuits remain elusive. Here, we report a role of the RtTg in startle reflex, a highly conserved innate defensive behaviour. Optogenetic activation of RtTg neurons evokes robust startle responses in mice. The glutamatergic neurons in the RtTg are significantly activated during acoustic startle reflexes (ASR). Chemogenetic inhibition of the RtTg glutamatergic neurons decreases the ASR amplitudes. Viral tracing reveals an ASR neural circuit that the cochlear nucleus carrying auditory information sends direct excitatory innervations to the RtTg glutamatergic neurons, which in turn project to spinal motor neurons. Together, our findings describe a functional role of RtTg and its related neural circuit in startle reflexes, and demonstrate how the RF connects auditory system with motor functions.
© 2021. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Giant neurons in the rat reticular formation: a sensorimotor interface in the elementary acoustic startle circuit?J Neurosci. 1994 Mar;14(3 Pt 1):1176-94. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.14-03-01176.1994. J Neurosci. 1994. PMID: 8120618 Free PMC article.
-
Habituation and sensitization of startle reflexes elicited electrically from the brainstem.Science. 1982 Nov 12;218(4573):688-90. doi: 10.1126/science.7134967. Science. 1982. PMID: 7134967
-
Neural organization in the brainstem circuit mediating the primary acoustic head startle: an electrophysiological study in the rat.Physiol Behav. 1990 Nov;48(5):727-39. doi: 10.1016/0031-9384(90)90218-s. Physiol Behav. 1990. PMID: 2082373
-
The acoustic startle response in rats--circuits mediating evocation, inhibition and potentiation.Behav Brain Res. 1997 Dec;89(1-2):35-49. doi: 10.1016/s0166-4328(97)02296-1. Behav Brain Res. 1997. PMID: 9475613 Review.
-
Brain stem circuits mediating prepulse inhibition of the startle reflex.Psychopharmacology (Berl). 2001 Jul;156(2-3):216-24. doi: 10.1007/s002130100794. Psychopharmacology (Berl). 2001. PMID: 11549224 Review.
Cited by
-
From innate to instructed: A new look at perceptual decision-making.Curr Opin Neurobiol. 2024 Jun;86:102871. doi: 10.1016/j.conb.2024.102871. Epub 2024 Apr 3. Curr Opin Neurobiol. 2024. PMID: 38569230 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Update on neurobiological mechanisms of fear: illuminating the direction of mechanism exploration and treatment development of trauma and fear-related disorders.Front Behav Neurosci. 2023 Aug 2;17:1216524. doi: 10.3389/fnbeh.2023.1216524. eCollection 2023. Front Behav Neurosci. 2023. PMID: 37600761 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Inhibition of RtTg neurons reverses methamphetamine-induced attention deficits.Acta Neuropathol Commun. 2024 Nov 22;12(1):179. doi: 10.1186/s40478-024-01890-0. Acta Neuropathol Commun. 2024. PMID: 39578917 Free PMC article.
-
The activation of catecholamine neurons in the rostral ventrolateral medulla drives ventricular remodeling after myocardial ischemia/reperfusion injury.Basic Res Cardiol. 2025 Jul 8. doi: 10.1007/s00395-025-01128-7. Online ahead of print. Basic Res Cardiol. 2025. PMID: 40627182
-
Advances in neural circuits of innate fear defense behavior.Zhejiang Da Xue Xue Bao Yi Xue Ban. 2023 Aug 1;52(5):653-661. doi: 10.3724/zdxbyxb-2023-0131. Zhejiang Da Xue Xue Bao Yi Xue Ban. 2023. PMID: 37899403 Free PMC article. Review. Chinese, English.
References
-
- Mangold, S. A. & M Das, J. Neuroanatomy, Reticular Formation. StatPearls. (2020). - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

