Metformin versus insulin therapy for gestational diabetes: Effects on offspring anthropometrics and metabolism at the age of 9 years: A follow-up study of two open-label, randomized controlled trials
- PMID: 34738701
- PMCID: PMC9299154
- DOI: 10.1111/dom.14589
Metformin versus insulin therapy for gestational diabetes: Effects on offspring anthropometrics and metabolism at the age of 9 years: A follow-up study of two open-label, randomized controlled trials
Abstract
Aims: To compare anthropometrics, and lipid and glucose metabolism in the 9-year-old offspring of mothers treated with metformin or insulin for gestational diabetes mellitus (GDM).
Materials and methods: This was a Finnish two-centre, 9-year follow-up study of two open-label, randomized controlled trials comparing the effects observed in the offspring of mothers who received metformin and insulin treatment for GDM. Measurements included anthropometrics, blood pressure, lipoproteins, and oral glucose tolerance tests. This study was registered with ClinicalTrials.gov, number NCT02417090.
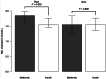
Results: At the age of 9 years 172 children (55% of the original study cohort, 82 from the metformin and 90 from the insulin group) participated in the study. No differences were found between the 9-year-old offspring groups in anthropometric variables, including body mass index and waist-to-height ratio. The offspring in the metformin group had higher high-density lipoprotein (HDL) cholesterol concentrations (1.72 vs. 1.54 mmol/L; P = 0.039) but lower low-density lipoprotein cholesterol (2.39 vs. 2.58 mmol/L; P = 0.046) and apolipoprotein B concentrations (0.63 vs. 0.67 g/L; P = 0.043) than the offspring in the insulin group. The difference in HDL cholesterol concentration was found to be significant only in boys (P = 0.003). The 2-hour glucose value in the oral glucose tolerance test was 0.6-mmol/L lower in boys from the metformin group than in those from the insulin group (P = 0.015).
Conclusions: Metformin treatment for GDM is associated with similar offspring growth and glucose metabolism but a more favourable lipid profile at the age of 9 years as compared to insulin treatment.
Keywords: anthropometry; gestational diabetes mellitus; glucose metabolism; lipid metabolism; metformin; offspring.
© 2021 The Authors. Diabetes, Obesity and Metabolism published by John Wiley & Sons Ltd.
Conflict of interest statement
There are no conflicts of interest to disclose.
Figures
References
-
- Committee on Practice Bulletins ‐ Obstetrics . ACOG practice bulletin no. 190: gestational diabetes mellitus. Obstet Gynecol. 2018;131:e49‐e64. - PubMed
-
- Yuen L, Saeedi P, Riaz M, et al. Projections of relevance of hyperglycaemia in pregnancy in 2019 and beyond: results from the international diabetes federation diabetes atlas, 9th edition. Diabetes Res Clin Pract. 2019;157:107841. - PubMed
-
- Metzger BE, Lowe LP, Dyer AR, et al. HAPO study cooperative research group. Hyperglycemia and adverse pregnancy outcomes. N Engl J Med. 2008;358:1991‐2002. - PubMed
-
- Burguet A. Long‐term outcome in children of mothers with gestational diabetes. Diabetes Metab. 2010;36:682‐694. - PubMed
-
- Dabelea D. The predisposition to obesity and diabetes in offspring of diabetic mothers. Diabetes Care. 2007;30:S169‐S174. - PubMed

