Long non-coding RNA LUADT1 promotes nasopharyngeal carcinoma cell proliferation and invasion by downregulating miR-1207-5p
- PMID: 34738862
- PMCID: PMC8810096
- DOI: 10.1080/21655979.2021.2001952
Long non-coding RNA LUADT1 promotes nasopharyngeal carcinoma cell proliferation and invasion by downregulating miR-1207-5p
Abstract
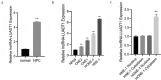
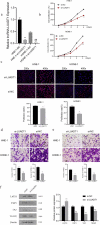
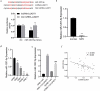
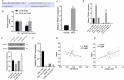
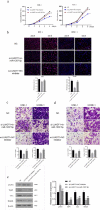
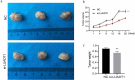
Nasopharyngeal carcinoma (NPC) is a typical type of malignant tumor. This research paper aims to study the function and mechanism of long non-coding RNA lung adenocarcinoma-related transcript 1 (lncRNA-LUADT1) in the progression of NPC. In this study, the expressions of lncRNA-LUADT1, miR-1207-5p, and TEAD1 in NPC tissues and cell lines were detected by RT-qPCR. Initially, the expression of lncRNA-LUADT1 and TEAD1 were significantly up-regulated in NPC tissues and cells, while miR-1207-5p was significantly down-regulated. Next, miR-1207-5p was confirmed to bind to lncRNA-LUADT1 or TEAD1 by bioinformatics and luciferase reporter assay. In addition, after interfering with lncRNA-LUADT1 expression, experiments of CCK8, EDU staining, and Transwell invasion were used to detect proliferation, invasion, and migration of NPC cells. The results showed that interfering with lncRNA-LUADT1 expression could inhibit the proliferation, invasion, and migration of NPC cells. Western blot showed that lncRNA-LUADT1 knockdown significantly decreased the expression of Hippo/YAP pathway protein (YAP1 and TAZ). However, interfering with the expression of miR-1207-5p reversed these results. In addition, the nude mouse tumor formation experiment suggested that low-expressed lncRNA-LUADT1 reduced the volume and weight of tumor tissues. In summary, lncRNA-LUADT1 down-regulation could inhibit NPC cell proliferation and invasion, which may be achieved through regulating miR-1207-5p expression and affecting TEAD1 expression, thus inhibiting the activation of Hippo/YAP signaling pathway.
Keywords: Hippo/YAP signaling pathway; Nasopharyngeal carcinoma; TEAD1; lncRNA-LUADT1; miR-1207-5p.
Conflict of interest statement
No potential conflict of interest was reported by the author(s).
Figures
Similar articles
-
LncRNA SNHG7 promotes the proliferation of nasopharyngeal carcinoma by miR-514a-5p/ELAVL1 axis.BMC Cancer. 2020 May 5;20(1):376. doi: 10.1186/s12885-020-06775-8. BMC Cancer. 2020. PMID: 32370736 Free PMC article.
-
Long non-coding RNA CASC15 promotes nasopharyngeal carcinoma cell proliferation and metastasis by downregulating miR-101-3p.Eur Rev Med Pharmacol Sci. 2019 Oct;23(20):8897-8904. doi: 10.26355/eurrev_201910_19285. Eur Rev Med Pharmacol Sci. 2019. Retraction in: Eur Rev Med Pharmacol Sci. 2021 Feb;25(3):1166. doi: 10.26355/eurrev_202102_24815. PMID: 31696476 Retracted.
-
LncRNA XIST knockdown suppresses the malignancy of human nasopharyngeal carcinoma through XIST/miRNA-148a-3p/ADAM17 pathway in vitro and in vivo.Biomed Pharmacother. 2020 Jan;121:109620. doi: 10.1016/j.biopha.2019.109620. Epub 2019 Nov 20. Biomed Pharmacother. 2020. PMID: 31810117
-
The Role of PTEN in Nasopharyngeal Carcinoma.Front Biosci (Landmark Ed). 2024 May 10;29(5):179. doi: 10.31083/j.fbl2905179. Front Biosci (Landmark Ed). 2024. PMID: 38812313 Review.
-
Emerging roles of lncRNA in Nasopharyngeal Carcinoma and therapeutic opportunities.Int J Biol Sci. 2022 Mar 28;18(7):2714-2728. doi: 10.7150/ijbs.70292. eCollection 2022. Int J Biol Sci. 2022. PMID: 35541920 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
A high level of the long non-coding RNA MCF2L-AS1 is associated with poor prognosis in breast cancer and MCF2L-AS1 activates YAP transcriptional activity to enhance breast cancer proliferation and metastasis.Bioengineered. 2022 May;13(5):13437-13451. doi: 10.1080/21655979.2022.2074108. Bioengineered. 2022. PMID: 36700469 Free PMC article.
-
TEA Domain Transcription Factor 1 Inhibits Ferroptosis and Sorafenib Sensitivity of Hepatocellular Carcinoma Cells.Dig Dis Sci. 2023 Jul;68(7):3070-3082. doi: 10.1007/s10620-023-07824-5. Epub 2023 Jan 21. Dig Dis Sci. 2023. PMID: 36680650 Free PMC article.
-
Relationship between long non-coding RNAs and Hippo signaling pathway in gastrointestinal cancers; molecular mechanisms and clinical significance.Heliyon. 2023 Dec 22;10(1):e23826. doi: 10.1016/j.heliyon.2023.e23826. eCollection 2024 Jan 15. Heliyon. 2023. PMID: 38226210 Free PMC article. Review.
-
miR-1204 Positioning in 8q24.21 Involved in the Tumorigenesis of Colorectal Cancer by Targeting MASPIN.Protein Pept Lett. 2024;31(7):544-558. doi: 10.2174/0109298665305114240718072029. Protein Pept Lett. 2024. PMID: 39082173
-
Hydroxyacyl-CoA dehydrogenase trifunctional multienzyme complex subunit beta gene as a tumour suppressor in stomach adenocarcinoma.Front Oncol. 2022 Nov 23;12:1069875. doi: 10.3389/fonc.2022.1069875. eCollection 2022. Front Oncol. 2022. PMID: 36518312 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Chen YP, Chan ATC, Le QT, et al. Nasopharyngeal carcinoma. Lancet. 2019;394:64–80. - PubMed
-
- Bray F, Ferlay J, Soerjomataram I, et al. Global cancer statistics 2018: GLOBOCAN estimates of incidence and mortality worldwide for 36 cancers in 185 countries. CA Cancer J Clin. 2018;68:394–424. - PubMed
-
- Razak AR, Siu LL, Liu FF, et al. Nasopharyngeal carcinoma: the next challenges. Eur J Cancer. 2010;46:1967–1978. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
