NOX4-derived ROS-induced overexpression of FOXM1 regulates aerobic glycolysis in glioblastoma
- PMID: 34740322
- PMCID: PMC8571893
- DOI: 10.1186/s12885-021-08933-y
NOX4-derived ROS-induced overexpression of FOXM1 regulates aerobic glycolysis in glioblastoma
Abstract
Background: Increased expression of the transcription factor Forkhead box M1 (FOXM1) has been reported to play an important role in the progression and development of multiple tumors, but the molecular mechanisms that regulate FOXM1 expression remain unknown, and the role of FOXM1 in aerobic glycolysis is still not clear.
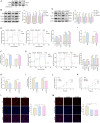
Methods: The expression of FOXM1 and NADPH oxidase 4 (NOX4) in normal brain tissues and glioma was detected in data from the TCGA database and in our specimens. The effect of NOX4 on the expression of FOXM1 was determined by Western blot, qPCR, reactive oxygen species (ROS) production assays, and luciferase assays. The functions of NOX4 and FOXM1 in aerobic glycolysis in glioblastoma cells were determined by a series of experiments, such as Western blot, extracellular acidification rate (ECAR), lactate production, and intracellular ATP level assays. A xenograft mouse model was established to test our findings in vivo.
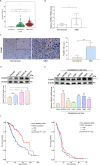
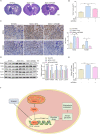
Results: The expression of FOXM1 and NOX4 was increased in glioma specimens compared with normal brain tissues and correlated with poor clinical outcomes. Aberrant mitochondrial reactive oxygen species (ROS) generation of NOX4 induced FOXM1 expression. Mechanistic studies demonstrated that NOX4-derived MitoROS exert their regulatory role on FOXM1 by mediating hypoxia-inducible factor 1α (HIF-1α) stabilization. Further research showed that NOX4-derived MitoROS-induced HIF-1α directly activates the transcription of FOXM1 and results in increased FOXM1 expression. Overexpression of NOX4 or FOXM1 promoted aerobic glycolysis, whereas knockdown of NOX4 or FOXM1 significantly suppressed aerobic glycolysis, in glioblastoma cells. NOX4-induced aerobic glycolysis was dependent on elevated FOXM1 expression, as FOXM1 knockdown abolished NOX4-induced aerobic glycolysis in glioblastoma cells both in vitro and in vivo.
Conclusion: Increased expression of FOXM1 induced by NOX4-derived MitoROS plays a pivotal role in aerobic glycolysis, and our findings suggest that inhibition of NOX4-FOXM1 signaling may present a potential therapeutic target for glioblastoma treatment.
Keywords: Aerobic glycolysis; FOXM1; Glioblastoma; NOX4; ROS.
© 2021. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no conflicts of interest.
Figures



References
-
- Liu Y, Cao Y, Zhang W, Bergmeier S, Qian Y, Akbar H, Colvin R, Ding J, Tong L, Wu S, Hines J, Chen X. A small-molecule inhibitor of glucose transporter 1 downregulates glycolysis, induces cell-cycle arrest, and inhibits cancer cell growth in vitro and in vivo. Mol Cancer Ther. 2012;11(8):1672–1682. doi: 10.1158/1535-7163.MCT-12-0131. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Pathria G, Scott DA, Feng Y, Sang Lee J, Fujita Y, Zhang G, et al. Targeting Glycolysis through Inhibition of Lactate Dehydrogenase Impairs Tumor Growth in Preclinical Models of Ewing Sarcoma. 2018;37(20). https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/31431459/. - PMC - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

