Oral prodrug of remdesivir parent GS-441524 is efficacious against SARS-CoV-2 in ferrets
- PMID: 34741049
- PMCID: PMC8571282
- DOI: 10.1038/s41467-021-26760-4
Oral prodrug of remdesivir parent GS-441524 is efficacious against SARS-CoV-2 in ferrets
Abstract
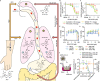
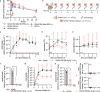
Remdesivir is an antiviral approved for COVID-19 treatment, but its wider use is limited by intravenous delivery. An orally bioavailable remdesivir analog may boost therapeutic benefit by facilitating early administration to non-hospitalized patients. This study characterizes the anti-SARS-CoV-2 efficacy of GS-621763, an oral prodrug of remdesivir parent nucleoside GS-441524. Both GS-621763 and GS-441524 inhibit SARS-CoV-2, including variants of concern (VOC) in cell culture and human airway epithelium organoids. Oral GS-621763 is efficiently converted to plasma metabolite GS-441524, and in lungs to the triphosphate metabolite identical to that generated by remdesivir, demonstrating a consistent mechanism of activity. Twice-daily oral administration of 10 mg/kg GS-621763 reduces SARS-CoV-2 burden to near-undetectable levels in ferrets. When dosed therapeutically against VOC P.1 gamma γ, oral GS-621763 blocks virus replication and prevents transmission to untreated contact animals. These results demonstrate therapeutic efficacy of a much-needed orally bioavailable analog of remdesivir in a relevant animal model of SARS-CoV-2 infection.
© 2021. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
All authors affiliated with Gilead Sciences may hold stock or stock options in Gilead Sciences Inc. R.K.P. was the principal investigator of a Gilead-sponsored research agreement with Georgia State University. He has received funding from Gilead Sciences Inc. to support parts of this work. All other authors declare no competing interests.
Figures


References
-
- U.S. Food & Drug Administration. FDA Approves First Treatment for COVID-19. https://www.fda.gov/news-events/press-announcements/fda-approves-first-t... (last accessed 06/06/2021), 2020).
-
- Mackman RL, et al. Prodrugs of a 1′-CN-4-Aza-7,9-dideazaadenosine C-Nucleoside Leading to the Discovery of Remdesivir (GS-5734) as a Potent Inhibitor of Respiratory Syncytial Virus with Efficacy in the African Green Monkey Model of RSV. J. Med. Chem. 2021;64:5001–5017. doi: 10.1021/acs.jmedchem.1c00071. - DOI - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
- R01 AI141222/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- R01 AI161175/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- AI141222/Division of Intramural Research, National Institute of Allergy and Infectious Diseases (Division of Intramural Research of the NIAID)
- AI153400/Division of Intramural Research, National Institute of Allergy and Infectious Diseases (Division of Intramural Research of the NIAID)
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous

