Optical biosensing of markers of mucosal inflammation
- PMID: 34743019
- PMCID: PMC9127977
- DOI: 10.1016/j.nano.2021.102476
Optical biosensing of markers of mucosal inflammation
Abstract
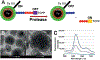
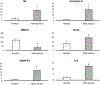
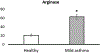
We report the design and adaptation of iron/iron oxide nanoparticle-based optical nanobiosensors for enzymes or cytokine/chemokines that are established biomarkers of lung diseases. These biomarkers comprise ADAM33, granzyme B, MMP-8, neutrophil elastase, arginase, chemokine (C-C motif) ligand 20 and interleukin-6. The synthesis of nanobiosensors for these seven biomarkers, their calibration with commercially available enzymes and cytokines/chemokines, as well as their validation using bronchoalveolar lavage (BAL) obtained from a mouse model of TLR3-mediated inflammation are discussed here. Exhaled Breath Condensate (EBC) is a minimally invasive approach for sampling airway fluid in the diagnosis and management of various lung diseases in humans (e.g., asthma, COPD and viral infections). We report the proof-of-concept of using human EBC in conjunction with nanobiosensors for diagnosis/monitoring airway inflammation. These findings suggest that, with nanosensor technology, human EBC can be utilized as a liquid biopsy to monitor inflammation/remodeling in lung disease.
Keywords: Iron/iron oxide core/shell nanoparticle; Lung inflammation; Nanodiagnostics; Nanomedicine; Optical biosensor.
Copyright © 2021 Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing financial interest.
Figures

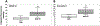
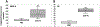

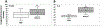
References
-
- Wiktorowicz JE, Jamaluddin M. Proteomic analysis of the asthmatic airway. Adv Exp Med Biol 2014;795:221–32. - PubMed
-
- Bossmann SH, Liquid biopsies for early cancer detection. In Biomaterials for cancer therapeutics, 2nd edition, Evolution and innovation, Park g, Ed. Elsevier: Amsterdam, 2020; pp. 233–259.
-
- Pisapia P, Malapelle U, Troncone G. Liquid biopsy and lung cancer. Acta Cytol 2019;63(6):489–96. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

