Effect of hydroxychloroquine sulfate on the gelation behavior, water mobility and structure of gelatin
- PMID: 34744314
- PMCID: PMC8565095
- DOI: 10.1016/j.colsurfa.2021.127849
Effect of hydroxychloroquine sulfate on the gelation behavior, water mobility and structure of gelatin
Abstract
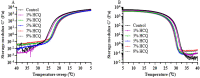
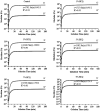
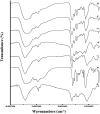
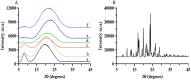
Hydroxychloroquine sulfate (HCQ) is a well-established antimalarial drug that has received considerable attention during the COVID-19 associated pneumonia epidemic. Gelatin is a multifunctional biomacromolecule with pharmaceutical applications and can be used to deliver HCQ. The effect of HCQ on the gelation behaviors, water mobility, and structure of gelatin was investigated to understand the interaction between the drug and its delivery carrier. The gel strength, hardness, gelling (Tg) and melting (Tm) temperatures, gelation rate (kgel), and water mobility of gelatin decreased with increasing amounts of HCQ. The addition of HCQ led to hydrogen bonding that interfered with triple helix formation in gelatin. Fourier transform infrared spectroscopy (FTIR) and X-ray diffractometer (XRD) analysis further confirmed that the interaction between HCQ and gelatin is primarily through hydrogen bonding. Atomic force microscopy (AFM) revealed that higher content of HCQ resulted in more and larger aggregates in gelatin. These results provide not only an important understanding of gelatin for drug delivery design but also a basis for the studying interactions between a drug and its delivery carrier.
Keywords: Gelatin; Gelation behavior; Hydroxychloroquine sulfate (HCQ); Interaction; Structure.
© 2021 Elsevier B.V. All rights reserved.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no known competing financial interests or personal relationships that could have appeared to influence the work reported in this paper.
Figures




References
-
- Dongala T., Katari N.K., Ettaboina S.K., Krishnan A., Tambuwala M.M., Dua K. In vitro dissolution profile at different biological pH conditions of hydroxychloroquine sulfate tablets is available for the treatment of COVID-19. Front. Mol. Biosci. 2021;7:1–6. doi: 10.3389/fmolb.2020.613393. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Magalhães G.A., Moura Neto E., Sombra V.G., Richter A.R., Abreu C.M.W.S., Feitosa J.P.A., Paula H.C.B., Goycoolea F.M., de Paula R.C.M. Chitosan/Sterculia striata polysaccharides nanocomplex as a potential chloroquine drug release device. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2016;88:244–253. doi: 10.1016/j.ijbiomac.2016.03.070. - DOI - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous
