Quantitative PCR to Discriminate Between Pneumocystis Pneumonia and Colonization in HIV and Non-HIV Immunocompromised Patients
- PMID: 34745031
- PMCID: PMC8564139
- DOI: 10.3389/fmicb.2021.729193
Quantitative PCR to Discriminate Between Pneumocystis Pneumonia and Colonization in HIV and Non-HIV Immunocompromised Patients
Abstract
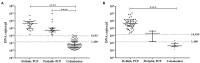
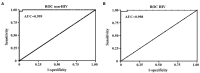
Pneumocystis pneumonia (PCP) is an opportunistic infection that commonly occurs in immunocompromised individuals. A definite diagnosis of PCP can be made only when the organism is identified in a respiratory specimen. It remains unclear whether qPCR can differentiate patients with PCP from those with Pneumocystis jirovecii colonization. In this study, we retrospectively collected data from HIV and non-HIV patients during 2013-2019. A diagnosis of definite, probable PCP, or PCP excluded was made based on clinical criteria, radiological reports, and three standard laboratory staining methods with blinding to qPCR data. Data from qPCR that was performed to determine the fungal burden (DNA copies/μl) in the BAL specimens of 69 HIV and 286 non-HIV patients were then obtained and reviewed. Receiver Operating Characteristic (ROC) curve analysis was performed to determine the upper and lower cut-off values for PCP diagnosis in HIV and non-HIV groups. In the non-HIV group, the lower cut-off value of 1,480 DNA copies/μl yielded a sensitivity of 100% (95% confidence interval [CI], 91.0-100), specificity of 72.9% (95% CI, 64.0-80.7), a positive predictive value (PPV) of 54.9% (95% CI, 47.6-62.1), and a negative predictive value (NPV) of 100% with Youden index of 0.73 for PCP diagnosis. In this group, the upper cut-off value of 9,655 DNA copies/μl showed the sensitivity of 100% (95% CI, 91.0-100) and specificity of 95.8% (95% CI, 90.4-98.6) with PPV of 88.6% (95% CI, 76.8-94.8) and a NPV of 100% with Youden index of 0.96 for PCP diagnosis. Regarding the HIV group, the lower cut-off value of 1,480 DNA copies/μl showed the sensitivity of 100% (95% CI, 92.5-100%) and specificity of 91.7% (95% CI, 61.5-99.8) with PPV of 97.9% (95% CI, 87.8-99.7) and a NPV of 100% with Youden index of 0.92 for PCP diagnosis. The sensitivity and specificity of the upper cut-off value of 12,718 DNA copies/μl in this group were 97.9% (95%CI, 88.7-100) and 100% (95%CI, 73.5-100), respectively. The values above the upper cut-off point had a PPV of 100% (95% CI, N/A) and a NPV of 92.3% (95% CI, 63.3-98.8) with Youden index of 0.98 for PCP diagnosis in the HIV group.
Keywords: PCP; Pneumocystis; Pneumocystis jirovecii; Pneumocystis pneumonia; colonization; definite PCP; probable PCP; qPCR.
Copyright © 2021 Sarasombath, Thongpiya, Chulanetra, Wijit, Chinabut, Ongrotchanakun, Jitmuang and Wanachiwanawin.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures
References
-
- Alanio A., Desoubeaux G., Sarfati C., Hamane S., Bergeron A., Azoulay E., et al. . (2011). Real-time PCR assay-based strategy for differentiation between active pneumocystis jirovecii pneumonia and colonization in immunocompromised patients. Clin. Microbiol. Infect. 17, 1531–1537. doi: 10.1111/j.1469-0691.2010.03400.x, PMID: - DOI - PubMed
-
- Botterel F., Cabaret O., Foulet F., Cordonnier C., Costa J.-M., Bretagne S. (2012). Clinical significance of quantifying pneumocystis jirovecii DNA by using real-time PCR in bronchoalveolar lavage fluid from immunocompromised patients. J. Clin. Microbiol. 50, 227–231. doi: 10.1128/JCM.06036-11, PMID: - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Damiani C., Le Gal S., Da Costa C., Virmaux M., Nevez G., Totet A. (2013). Combined quantification of pulmonary pneumocystis jirovecii DNA and serum (1->3)-β-D-glucan for differential diagnosis of pneumocystis pneumonia and pneumocystis colonization. J. Clin. Microbiol. 51, 3380–3388. doi: 10.1128/JCM.01554-13, PMID: - DOI - PMC - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

