Premature Senescence and Telomere Shortening Induced by Oxidative Stress From Oxalate, Calcium Oxalate Monohydrate, and Urine From Patients With Calcium Oxalate Nephrolithiasis
- PMID: 34745087
- PMCID: PMC8566732
- DOI: 10.3389/fimmu.2021.696486
Premature Senescence and Telomere Shortening Induced by Oxidative Stress From Oxalate, Calcium Oxalate Monohydrate, and Urine From Patients With Calcium Oxalate Nephrolithiasis
Abstract
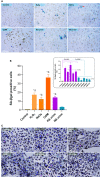
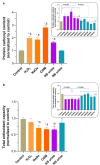
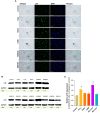
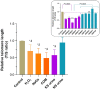
Oxidative stress, a well-known cause of stress-induced premature senescence (SIPS), is increased in patients with calcium oxalate (CaOx) kidney stones (KS). Oxalate and calcium oxalate monohydrate (COM) induce oxidative stress in renal tubular cells, but to our knowledge, their effect on SIPS has not yet been examined. Here, we examined whether oxalate, COM, or urine from patients with CaOx KS could induce SIPS and telomere shortening in human kidney (HK)-2 cells, a proximal tubular renal cell line. Urine from age- and sex-matched individuals without stones was used as a control. In sublethal amounts, H2O2, oxalate, COM, and urine from those with KS evoked oxidative stress in HK-2 cells, indicated by increased protein carbonyl content and decreased total antioxidant capacity, but urine from those without stones did not. The proportion of senescent HK-2 cells, as indicated by SA-βgal staining, increased after treatment with H2O2, oxalate, COM, and urine from those with KS. Expression of p16 was higher in HK-2 cells treated with H2O2, oxalate, COM, and urine from those with KS than it was in cells treated with urine from those without stones and untreated controls. p16 was upregulated in the SA-βgal positive cells. Relative telomere length was shorter in HK-2 cells treated with H2O2, oxalate, COM, and urine from those with KS than that in cells treated with urine from those without stones and untreated controls. Transcript expression of shelterin components (TRF1, TRF2 and POT1) was decreased in HK-2 cells treated with H2O2, oxalate, COM, and urine from those with KS, in which case the expression was highest. Urine from those without KS did not significantly alter TRF1, TRF2, and POT1 mRNA expression in HK-2 cells relative to untreated controls. In conclusion, oxalate, COM, and urine from patients with CaOx KS induced SIPS and telomere shortening in renal tubular cells. SIPS induced by a lithogenic milieu may result from upregulation of p16 and downregulation of shelterin components, specifically POT1, and might contribute, at least in part, to the development of CaOx KS.
Keywords: calcium oxalate; cellular senescence; kidney calculi; nephrolithiasis; oxalates; oxidative stress; urine.
Copyright © 2021 Chuenwisad, More-krong, Tubsaeng, Chotechuang, Srisa-Art, Storer and Boonla.
Conflict of interest statement
CB and NC are inventors of HydroZitLa, an antioxidant intervention for patients with kidney stones (patent pending). Chulalongkorn University and the inventors own the intellectual property for HydroZitLa. The remaining authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures
Similar articles
-
miR-155-5p Promotes Oxalate- and Calcium-Induced Kidney Oxidative Stress Injury by Suppressing MGP Expression.Oxid Med Cell Longev. 2020 Mar 4;2020:5863617. doi: 10.1155/2020/5863617. eCollection 2020. Oxid Med Cell Longev. 2020. PMID: 32215174 Free PMC article.
-
Mitochondrial enzyme HIBADH protects against calcium oxalate nephrolithiasis by modulating oxidative stress and apoptosis.Arch Biochem Biophys. 2025 Aug;770:110452. doi: 10.1016/j.abb.2025.110452. Epub 2025 May 5. Arch Biochem Biophys. 2025. PMID: 40334962
-
Mucin 4 Gene Silencing Reduces Oxidative Stress and Calcium Oxalate Crystal Formation in Renal Tubular Epithelial Cells Through the Extracellular Signal-Regulated Kinase Signaling Pathway in Nephrolithiasis Rat Model.Kidney Blood Press Res. 2018;43(3):820-835. doi: 10.1159/000490136. Epub 2018 May 25. Kidney Blood Press Res. 2018. Retraction in: Kidney Blood Press Res. 2022;47(9):592. doi: 10.1159/000526608. PMID: 29843125 Retracted.
-
Nephrolithiasis: a consequence of renal epithelial cell exposure to oxalate and calcium oxalate crystals.Mol Urol. 2000 Winter;4(4):305-12. Mol Urol. 2000. PMID: 11156696 Review.
-
The significance of reactive oxygen species in the formation of calcium oxalate stones and the protective effects of antioxidants on the kidneys.Front Immunol. 2025 May 21;16:1540075. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2025.1540075. eCollection 2025. Front Immunol. 2025. PMID: 40469275 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Possible molecular mechanisms underlying the development of atherosclerosis in cancer survivors.Front Cardiovasc Med. 2023 Jun 2;10:1186679. doi: 10.3389/fcvm.2023.1186679. eCollection 2023. Front Cardiovasc Med. 2023. PMID: 37332576 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Metabolic regulation of endothelial senescence.Front Cardiovasc Med. 2023 Aug 15;10:1232681. doi: 10.3389/fcvm.2023.1232681. eCollection 2023. Front Cardiovasc Med. 2023. PMID: 37649668 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Telomere Attrition in Induced Pluripotent Stem Cell-Derived Neurons From ALS/FTD-Related C9ORF72 Repeat Expansion Carriers.Front Cell Dev Biol. 2022 Jun 13;10:874323. doi: 10.3389/fcell.2022.874323. eCollection 2022. Front Cell Dev Biol. 2022. PMID: 35769259 Free PMC article.
-
Premature senescence and cardiovascular disease following cancer treatments: mechanistic insights.Front Cardiovasc Med. 2023 Sep 14;10:1212174. doi: 10.3389/fcvm.2023.1212174. eCollection 2023. Front Cardiovasc Med. 2023. PMID: 37781317 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Decreased telomere length in a subgroup of young individuals with bipolar disorders: replication in the FACE-BD cohort and association with the shelterin component POT1.Transl Psychiatry. 2024 Mar 1;14(1):131. doi: 10.1038/s41398-024-02824-z. Transl Psychiatry. 2024. PMID: 38429270 Free PMC article.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Supplementary concepts
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

