An Internet of Medical Things-Based Model for Real-Time Monitoring and Averting Stroke Sensors
- PMID: 34745488
- PMCID: PMC8566034
- DOI: 10.1155/2021/1233166
An Internet of Medical Things-Based Model for Real-Time Monitoring and Averting Stroke Sensors
Retraction in
-
Retracted: An Internet of Medical Things-Based Model for Real-Time Monitoring and Averting Stroke Sensors.J Healthc Eng. 2023 Oct 11;2023:9801737. doi: 10.1155/2023/9801737. eCollection 2023. J Healthc Eng. 2023. PMID: 37860393 Free PMC article.
Abstract
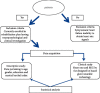
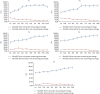
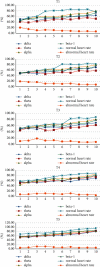
In recent years, neurological diseases have become a standout amongst all the other diseases and are the most important reasons for mortality and morbidity all over the world. The current study's aim is to conduct a pilot study for testing the prototype of the designed glove-wearable technology that could detect and analyze the heart rate and EEG for better management and avoiding stroke consequences. The qualitative, clinical experimental method of assessment was explored by incorporating use of an IoT-based real-time assessing medical glove that was designed using heart rate-based and EEG-based sensors. We conducted structured interviews with 90 patients, and the results of the interviews were analyzed by using the Barthel index and were grouped accordingly. Overall, the proportion of patients who followed proper daily heart rate recording behavior went from 46.9% in the first month of the trial to 78.2% after 3-10 months of the interventions. Meanwhile, the percentage of individuals having an irregular heart rate fell from 19.5% in the first month of the trial to 9.1% after 3-10 months of intervention research. In T5, we found that delta relative power decreased by 12.1% and 5.8% compared with baseline at 3 and at 6 months and an average increase was 24.3 ± 0.08. Beta-1 remained relatively steady, while theta relative power grew by 7% and alpha relative power increased by 31%. The T1 hemisphere had greater mean values of delta and theta relative power than the T5 hemisphere. For alpha (p < 0.05) and beta relative power, the opposite pattern was seen. The distinction was statistically significant for delta (p < 0.001), alpha (p < 0.01), and beta-1 (p < 0.05) among T1 and T5 patient groups. In conclusion, our single center-based study found that such IoT-based real-time medical monitoring devices significantly reduce the complexity of real-time monitoring and data acquisition processes for a healthcare provider and thus provide better healthcare management. The emergence of significant risks and controlling mechanisms can be improved by boosting the awareness. Furthermore, it identifies the high-risk factors besides facilitating the prevention of strokes. The EEG-based brain-computer interface has a promising future in upcoming years to avert DALY.
Copyright © 2021 Hatim Z. Almarzouki et al.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that there are no conflicts of interest regarding the publication of this paper.
Figures

Similar articles
-
An IoMT-Based Approach for Real-Time Monitoring Using Wearable Neuro-Sensors.J Healthc Eng. 2023 Feb 13;2023:1066547. doi: 10.1155/2023/1066547. eCollection 2023. J Healthc Eng. 2023. PMID: 36814546 Free PMC article.
-
IoT-based wearable health monitoring device and its validation for potential critical and emergency applications.Front Public Health. 2023 Jun 16;11:1188304. doi: 10.3389/fpubh.2023.1188304. eCollection 2023. Front Public Health. 2023. PMID: 37397724 Free PMC article.
-
Feasibility and efficacy of wearable devices for upper limb rehabilitation in patients with chronic stroke: a randomized controlled pilot study.Eur J Phys Rehabil Med. 2018 Jun;54(3):388-396. doi: 10.23736/S1973-9087.17.04691-3. Epub 2017 Jun 19. Eur J Phys Rehabil Med. 2018. PMID: 28627862 Clinical Trial.
-
A Systematic Review and Implementation of IoT-Based Pervasive Sensor-Enabled Tracking System for Dementia Patients.J Med Syst. 2019 Jul 17;43(9):287. doi: 10.1007/s10916-019-1417-z. J Med Syst. 2019. PMID: 31317281
-
A Systematic Review of Wearable Sensors and IoT-Based Monitoring Applications for Older Adults - a Focus on Ageing Population and Independent Living.J Med Syst. 2019 Jun 15;43(8):233. doi: 10.1007/s10916-019-1365-7. J Med Syst. 2019. PMID: 31203472
Cited by
-
Extracting Behavior Identification Features for Monitoring and Managing Speech-Dependent Smart Mental Illness Healthcare Systems.Comput Intell Neurosci. 2022 May 6;2022:8579640. doi: 10.1155/2022/8579640. eCollection 2022. Comput Intell Neurosci. 2022. Retraction in: Comput Intell Neurosci. 2023 Jul 26;2023:9794125. doi: 10.1155/2023/9794125. PMID: 35535193 Free PMC article. Retracted.
-
Retracted: An Internet of Medical Things-Based Model for Real-Time Monitoring and Averting Stroke Sensors.J Healthc Eng. 2023 Oct 11;2023:9801737. doi: 10.1155/2023/9801737. eCollection 2023. J Healthc Eng. 2023. PMID: 37860393 Free PMC article.
-
[An emerging discipline: brain-computer interfaces medicine].Sheng Wu Yi Xue Gong Cheng Xue Za Zhi. 2024 Aug 25;41(4):641-649. doi: 10.7507/1001-5515.202310028. Sheng Wu Yi Xue Gong Cheng Xue Za Zhi. 2024. PMID: 39218588 Free PMC article. Review. Chinese.
-
Supervised Computer-Aided Diagnosis (CAD) Methods for Classifying Alzheimer's Disease-Based Neurodegenerative Disorders.Comput Math Methods Med. 2022 May 23;2022:9092289. doi: 10.1155/2022/9092289. eCollection 2022. Comput Math Methods Med. 2022. Retraction in: Comput Math Methods Med. 2023 Dec 13;2023:9759262. doi: 10.1155/2023/9759262. PMID: 35651921 Free PMC article. Retracted.
-
Glaucoma Detection and Classification Using Improved U-Net Deep Learning Model.Healthcare (Basel). 2022 Dec 9;10(12):2497. doi: 10.3390/healthcare10122497. Healthcare (Basel). 2022. PMID: 36554021 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Seners P., Turc G., Oppenheim C., Baron J.-C. Incidence, causes and predictors of neurological deterioration occurring within 24 h following acute ischaemic stroke: a systematic review with pathophysiological implications. Journal of Neurology, Neurosurgery & Psychiatry . 2015;86(1):87–94. doi: 10.1136/jnnp-2014-308327. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Chen L., Jagota V., Kumar A. Research on optimization of scientific research performance management based on BP neural network. International Journal of System Assurance Engineering and Management . 2021;12 doi: 10.1007/s13198-021-01263-z. - DOI
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

