IL-1beta promotes the age-associated decline of beta cell function
- PMID: 34746709
- PMCID: PMC8554531
- DOI: 10.1016/j.isci.2021.103250
IL-1beta promotes the age-associated decline of beta cell function
Abstract
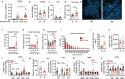
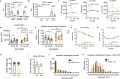
Aging is the prime risk factor for the development of type 2 diabetes. We investigated the role of the interleukin-1 (IL-1) system on insulin secretion in aged mice. During aging, expression of the protective IL-1 receptor antagonist decreased in islets, whereas IL-1beta gene expression increased specifically in the CD45 + islet immune cell fraction. One-year-old mice with a whole-body knockout of IL-1beta had higher insulin secretion in vivo and in isolated islets, along with enhanced proliferation marker Ki67 and elevated size and number of islets. Myeloid cell-specific IL-1beta knockout preserved glucose-stimulated insulin secretion during aging, whereas it declined in control mice. Isolated islets from aged myeloIL-1beta ko mice secreted more insulin along with increased expression of Ins2, Kir6.2, and of the cell-cycle gene E2f1. IL-1beta treatment of isolated islets reduced E2f1, Ins2, and Kir6.2 expression in beta cells. We conclude that IL-1beta contributes the age-associated decline of beta cell function.
Keywords: Cell biology; Cellular physiology; Physiology.
© 2021 The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
M.Y.D. is listed as the inventor on a patent filed in 2003 for the use of an IL-1 receptor antagonist for the treatment of or prophylaxis for type 2 diabetes.
Figures





References
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

