An H3F3A K27M-mutation in a sonic hedgehog medulloblastoma
- PMID: 34747078
- PMCID: PMC9048514
- DOI: 10.1111/bpa.13024
An H3F3A K27M-mutation in a sonic hedgehog medulloblastoma
Abstract
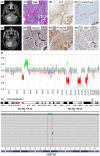
Medulloblastomas are malignant embryonal brain tumours that may harbour mutations in histone-modifying genes, while mutations in histone genes have not been detected to date. We here describe the first SHH medulloblastoma with H3 K27M mutation. This may have diagnostic implications as H3 K27M mutations are the hallmark of diffuse midline gliomas, H3 K27M mutant, WHO grade IV. Medulloblastomas arise in midline structures and thus must not be mistaken for DMG when using an antibody detecting the H3 K27M mutation.
Keywords: H3F3A; H3K27me3; H3 K27M; NGS; SHH; medulloblastoma.
© 2021 The Authors. Brain Pathology published by John Wiley & Sons Ltd on behalf of International Society of Neuropathology.
Conflict of interest statement
None to declare.
Figures
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

