Classifying chest CT images as COVID-19 positive/negative using a convolutional neural network ensemble model and uniform experimental design method
- PMID: 34749629
- PMCID: PMC8574139
- DOI: 10.1186/s12859-021-04083-x
Classifying chest CT images as COVID-19 positive/negative using a convolutional neural network ensemble model and uniform experimental design method
Abstract
Background: To classify chest computed tomography (CT) images as positive or negative for coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19) quickly and accurately, researchers attempted to develop effective models by using medical images.
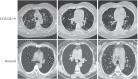
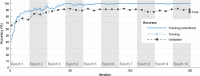
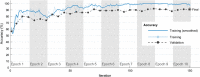
Results: A convolutional neural network (CNN) ensemble model was developed for classifying chest CT images as positive or negative for COVID-19. To classify chest CT images acquired from COVID-19 patients, the proposed COVID19-CNN ensemble model combines the use of multiple trained CNN models with a majority voting strategy. The CNN models were trained to classify chest CT images by transfer learning from well-known pre-trained CNN models and by applying their algorithm hyperparameters as appropriate. The combination of algorithm hyperparameters for a pre-trained CNN model was determined by uniform experimental design. The chest CT images (405 from COVID-19 patients and 397 from healthy patients) used for training and performance testing of the COVID19-CNN ensemble model were obtained from an earlier study by Hu in 2020. Experiments showed that, the COVID19-CNN ensemble model achieved 96.7% accuracy in classifying CT images as COVID-19 positive or negative, which was superior to the accuracies obtained by the individual trained CNN models. Other performance measures (i.e., precision, recall, specificity, and F1-score) obtained bythe COVID19-CNN ensemble model were higher than those obtained by individual trained CNN models.
Conclusions: The COVID19-CNN ensemble model had superior accuracy and excellent capability in classifying chest CT images as COVID-19 positive or negative.
Keywords: Algorithm hyperparameter; COVID-19; Chest computed tomography image; Convolutional neural network; Ensemble model.
© 2021. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Figures




References
-
- Gozes O, Frid-Adar M, Greenspan H, Browning P, Zhang H, Ji W, Bernheim A. Rapid AI development cycle for the coronavirus (COVID-19) pandemic: initial results for automated detection and patient monitoring using deep learning CT image analysis. Submitted to Radiology: Artificial Intelligence; 2020. p. 1–22.
-
- Shan F, Gao Y, Wang J, Shi W, Shi N, Han M, Xue Z, Shi Y. Lung infection quantification of COVID-19 in CT images with deep learning. 2020, p. 1–19. arXiv preprint arXiv:2003.04655.
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

