Design of lung nodules segmentation and recognition algorithm based on deep learning
- PMID: 34749636
- PMCID: PMC8576909
- DOI: 10.1186/s12859-021-04234-0
Design of lung nodules segmentation and recognition algorithm based on deep learning
Abstract
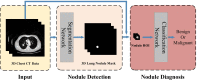
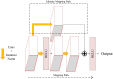
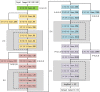
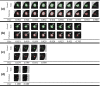
Background: Accurate segmentation and recognition algorithm of lung nodules has great important value of reference for early diagnosis of lung cancer. An algorithm is proposed for 3D CT sequence images in this paper based on 3D Res U-Net segmentation network and 3D ResNet50 classification network. The common convolutional layers in encoding and decoding paths of U-Net are replaced by residual units while the loss function is changed to Dice loss after using cross entropy loss to accelerate network convergence. Since the lung nodules are small and rich in 3D information, the ResNet50 is improved by replacing the 2D convolutional layers with 3D convolutional layers and reducing the sizes of some convolution kernels, 3D ResNet50 network is obtained for the diagnosis of benign and malignant lung nodules.
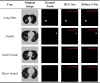
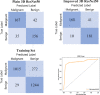
Results: 3D Res U-Net was trained and tested on 1044 CT subcases in the LIDC-IDRI database. The segmentation result shows that the Dice coefficient of 3D Res U-Net is above 0.8 for the segmentation of lung nodules larger than 10 mm in diameter. 3D ResNet50 was trained and tested on 2960 lung nodules in the LIDC-IDRI database. The classification result shows that the diagnostic accuracy of 3D ResNet50 is 87.3% and AUC is 0.907.
Conclusion: The 3D Res U-Net module improves segmentation performance significantly with the comparison of 3D U-Net model based on residual learning mechanism. 3D Res U-Net can identify small nodules more effectively and improve its segmentation accuracy for large nodules. Compared with the original network, the classification performance of 3D ResNet50 is significantly improved, especially for small benign nodules.
Keywords: Convolutional neural network; Image classification; Image segmentation; Lung nodule; Residual learning; U-Net.
© 2021. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Figures





References
-
- Siegel RL, Miller KD, Jemal A. Cancer statistics, 2019. CA Cancer J Clin. 2019;69(1):7–34. - PubMed
-
- Li B, Chen K, Peng G, Guo Y, Tian L, Ou S, et al. Segmentation of ground glass opacity pulmonary nodules using an integrated active contour model with wavelet energy-based adaptive local energy and posterior probability-based speed function. Mater Express. 2016;6(4):317–327. doi: 10.1166/mex.2016.1311. - DOI
-
- Mao Q, Zhao S, Gong T, Zheng Q. An Effective Hybrid Windowed Fourier Filtering and Fuzzy C-Mean for Pulmonary Nodule Segmentation. J Med Imaging Health Inf. 2018;8(1):72–77. doi: 10.1166/jmihi.2018.2235. - DOI
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

