Binding affinity prediction for protein-ligand complex using deep attention mechanism based on intermolecular interactions
- PMID: 34749664
- PMCID: PMC8576937
- DOI: 10.1186/s12859-021-04466-0
Binding affinity prediction for protein-ligand complex using deep attention mechanism based on intermolecular interactions
Abstract
Background: Accurate prediction of protein-ligand binding affinity is important for lowering the overall cost of drug discovery in structure-based drug design. For accurate predictions, many classical scoring functions and machine learning-based methods have been developed. However, these techniques tend to have limitations, mainly resulting from a lack of sufficient energy terms to describe the complex interactions between proteins and ligands. Recent deep-learning techniques can potentially solve this problem. However, the search for more efficient and appropriate deep-learning architectures and methods to represent protein-ligand complex is ongoing.
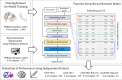
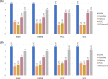
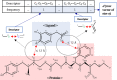
Results: In this study, we proposed a deep-neural network model to improve the prediction accuracy of protein-ligand complex binding affinity. The proposed model has two important features, descriptor embeddings with information on the local structures of a protein-ligand complex and an attention mechanism to highlight important descriptors for binding affinity prediction. The proposed model performed better than existing binding affinity prediction models on most benchmark datasets.
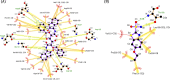
Conclusions: We confirmed that an attention mechanism can capture the binding sites in a protein-ligand complex to improve prediction performance. Our code is available at https://github.com/Blue1993/BAPA .
Keywords: Attention mechanism; Binding affinity; Protein–ligand complex; Structure-based drug design.
© 2021. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Figures
References
-
- Kroemer RT. Structure-based drug design: docking and scoring. Curr Protein Pept Sci. 2007;8(4):312–328. - PubMed
-
- Li S, Xi L, Wang C, Li J, Lei B, Liu H, Yao X. A novel method for protein-ligand binding affinity prediction and the related descriptors exploration. J Comput Chem. 2009;30(6):900–909. - PubMed
-
- DiMasi JA, Hansen RW, Grabowski HG. The price of innovation: new estimates of drug development costs. J Health Econ. 2003;22(2):151–185. - PubMed
-
- Ewing TJ, Makino S, Skillman AG, Kuntz ID. DOCK 40: search strategies for automated molecular docking of flexible molecule databases. J Comput Aided Mol Design. 2001;15(5):411–428. - PubMed
-
- Jones G, Willett P, Glen RC, Leach AR, Taylor R. Development and validation of a genetic algorithm for flexible docking. J Mol Biol. 1997;267(3):727–748. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

