Fenebrutinib in H1 antihistamine-refractory chronic spontaneous urticaria: a randomized phase 2 trial
- PMID: 34750553
- PMCID: PMC8604722
- DOI: 10.1038/s41591-021-01537-w
Fenebrutinib in H1 antihistamine-refractory chronic spontaneous urticaria: a randomized phase 2 trial
Abstract
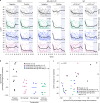
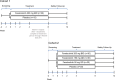
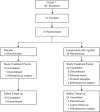
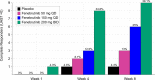
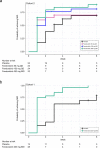
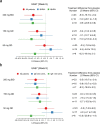
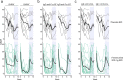
Bruton's tyrosine kinase (BTK) is crucial for FcεRI-mediated mast cell activation and essential for autoantibody production by B cells in chronic spontaneous urticaria (CSU). Fenebrutinib, an orally administered, potent, highly selective, reversible BTK inhibitor, may be effective in CSU. This double-blind, placebo-controlled, phase 2 trial (EudraCT ID 2016-004624-35 ) randomized 93 adults with antihistamine-refractory CSU to 50 mg daily, 150 mg daily and 200 mg twice daily of fenebrutinib or placebo for 8 weeks. The primary end point was change from baseline in urticaria activity score over 7 d (UAS7) at week 8. Secondary end points were the change from baseline in UAS7 at week 4 and the proportion of patients well-controlled (UAS7 ≤ 6) at week 8. Fenebrutinib efficacy in patients with type IIb autoimmunity and effects on IgG-anti-FcεRI were exploratory end points. Safety was also evaluated. The primary end point was met, with dose-dependent improvements in UAS7 at week 8 occurring at 200 mg twice daily and 150 mg daily, but not at 50 mg daily of fenebrutinib versus placebo. Asymptomatic, reversible grade 2 and 3 liver transaminase elevations occurred in the fenebrutinib 150 mg daily and 200 mg twice daily groups (2 patients each). Fenebrutinib diminished disease activity in patients with antihistamine-refractory CSU, including more patients with refractory type IIb autoimmunity. These results support the potential use of BTK inhibition in antihistamine-refractory CSU.
© 2021. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
M. Metz reports receiving honoraria as a speaker and/or consultant for Amgen, Aralez, argenx, Moxie, Novartis, Roche, Sanofi, Shire and Uriach. G.S. reports serving as a principal investigator for Genentech, Novartis, CSL Behring, Shire, Sanofi, AstraZeneca, DBV Technologies, Aimmune Therapeutics, Greencross, Kedrion, ALK-Abelló, Stallergenes, LEO Pharma, Amgen, BioCryst, Regeneron and Cliantha; serving on advisory boards for Novartis, CSL Behring, Shire, Sanofi, Aralez, Pediapharm and AstraZeneca; serving as a speaker for Novartis, Sanofi, Aralez, Pediapharm, Genentech and AstraZeneca; receiving personal fees from Novartis, CSL Behring, Shire, Sanofi, Aralez, Pediapharm and AstraZeneca. T.T. reports receiving funding from Genentech to his institution for the conduct of this study. W.H.Y. reports receiving speakers’ fees from Novartis, Merck, CSL Behring, Takeda (Shire) and AstraZeneca; serving on advisory boards for Novartis, Takeda (Shire), CSL Behring, Sanofi, BioCryst and Merck; and receiving research grants from Novartis, Takeda (Shire), CSL Behring, BioCryst, AstraZeneca, Regeneron, Sanofi, Genentech, Glenmark, AnaptysBio, Dermira, Galderma, ALK, DBV Technologies, Aimmune Therapeutics, Colgene and Pharming. J.J.L., H.J.C., J.G., L.W.C., T.C., T.B., D.J.H. and T.T.L. are current or former employees of Genentech, a member of the Roche group, at the time this work was performed and own/owned Roche stock and/or options. L.W.C. is currently an employee of Principia Biopharma and owns Principia Biopharma stock and/or options. D.J.H. owns Principia Biopharma stock. T.T.L. is currently an employee of DiCE Molecules. M. Maurer is or recently was a speaker and/or advisor for and/or has received research funding from Allakos, Amgen, Aralez, AstraZeneca, Celldex, Centogene, CSL Behring, FAES, Genentech, GI Innovation, Innate Pharma, Kyowa Kirin, LEO Pharma, Lilly, Menarini, Moxie, Merck Sharp & Dohme, Novartis, Roche, Sanofi/Regeneron, Third Harmonic Bio, UCB and Uriach. R.G. and P.S. declare no competing interests.
Figures


References
-
- Zuberbier T, et al. The EAACI/GA²LEN/EDF/WAO guideline for the definition, classification, diagnosis and management of urticaria. Allergy. 2018;73:1393–1414. - PubMed
-
- Fricke J, et al. Prevalence of chronic urticaria in children and adults across the globe: systematic review with meta-analysis. Allergy. 2020;75:423–432. - PubMed
-
- Kolkhir P, et al. Autoimmune chronic spontaneous urticaria: what we know and what we do not know. J. Allergy Clin. Immunol. 2017;139:1772–1781.e1. - PubMed
-
- Schmetzer O, et al. IL-24 is a common and specific autoantigen of IgE in patients with chronic spontaneous urticaria. J. Allergy Clin. Immunol. 2018;142:876–882. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous

