Typical m. triceps surae morphology and architecture measurement from 0 to 18 years: A narrative review
- PMID: 34750816
- PMCID: PMC8930835
- DOI: 10.1111/joa.13584
Typical m. triceps surae morphology and architecture measurement from 0 to 18 years: A narrative review
Abstract
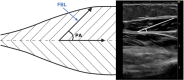
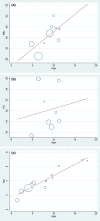
The aim of this review was to report on the imaging modalities used to assess morphological and architectural properties of the m. triceps surae muscle in typically developing children, and the available reliability analyses. Scopus and MEDLINE (Pubmed) were searched systematically for all original articles published up to September 2020 measuring morphological and architectural properties of the m. triceps surae in typically developing children (18 years or under). Thirty eligible studies were included in this analysis, measuring fibre bundle length (FBL) (n = 11), pennation angle (PA) (n = 10), muscle volume (MV) (n = 16) and physiological cross-sectional area (PCSA) (n = 4). Three primary imaging modalities were utilised to assess these architectural parameters in vivo: two-dimensional ultrasound (2DUS; n = 12), three-dimensional ultrasound (3DUS; n = 9) and magnetic resonance imaging (MRI; n = 6). The mean age of participants ranged from 1.4 years to 18 years old. There was an apparent increase in m. gastrocnemius medialis MV and pCSA with age; however, no trend was evident with FBL or PA. Analysis of correlations of muscle variables with age was limited by a lack of longitudinal data and methodological variations between studies affecting outcomes. Only five studies evaluated the reliability of the methods. Imaging methodologies such as MRI and US may provide valuable insight into the development of skeletal muscle from childhood to adulthood; however, variations in methodological approaches can significantly influence outcomes. Researchers wishing to develop a model of typical muscle development should carry out longitudinal architectural assessment of all muscles comprising the m. triceps surae utilising a consistent approach that minimises confounding errors.
Keywords: architectural properties; imaging modalities; musculoskeletal development; paediatrics; triceps surae.
© 2021 The Authors. Journal of Anatomy published by John Wiley & Sons Ltd on behalf of Anatomical Society.
Figures


References
-
- Agur, A.M. , Ng‐Thow‐Hing, V. , Ball, K.A. , Fiume, E. & McKee, N.H. (2003) Documentation and three‐dimensional modelling of human soleus muscle architecture. Clinical Anatomy, 16(4), 285–293. - PubMed
-
- Albracht, K. , Arampatzis, A. & Baltzopoulos, V. (2008) Assessment of muscle volume and physiological cross‐sectional area of the human triceps surae muscle in vivo. Journal of Biomechanics, 41(10), 2211–2218. - PubMed
-
- Barber, L. , Barrett, R. & Lichtwark, G. (2009) Validation of a freehand 3D ultrasound system for morphological measures of the medial gastrocnemius muscle. Journal of Biomechanics, 42(9), 1313–1319. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

