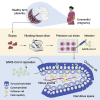
SARS-CoV-2 can infect and propagate in human placenta explants
- PMID: 34751258
- PMCID: PMC8566476
- DOI: 10.1016/j.xcrm.2021.100456
SARS-CoV-2 can infect and propagate in human placenta explants
Abstract
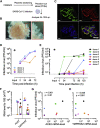
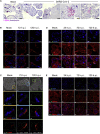
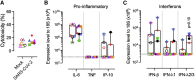
The ongoing SARS-CoV-2 pandemic continues to lead to high morbidity and mortality. During pregnancy, severe maternal and neonatal outcomes and placental pathological changes have been described. We evaluate SARS-CoV-2 infection at the maternal-fetal interface using precision-cut slices (PCSs) of human placenta. Remarkably, exposure of placenta PCSs to SARS-CoV-2 leads to a full replication cycle with infectious virus release. Moreover, the susceptibility of placental tissue to SARS-CoV-2 replication relates to the expression levels of ACE2. Viral proteins and/or viral RNA are detected in syncytiotrophoblasts, cytotrophoblasts, villous stroma, and possibly Hofbauer cells. While SARS-CoV-2 infection of placenta PCSs does not cause a detectable cytotoxicity or a pro-inflammatory cytokine response, an upregulation of one order of magnitude of interferon type III transcripts is measured. In conclusion, our data demonstrate the capacity of SARS-CoV-2 to infect and propagate in human placenta and constitute a basis for further investigation of SARS-CoV-2 biology at the maternal-fetal interface.
Keywords: COVID-19; SARS-CoV-2; coronavirus; pandemic; placenta; pregnancy; vertical transmission.
© 2021 The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

