Trends in seroprevalence of SARS-CoV-2 and infection fatality rate in the Norwegian population through the first year of the COVID-19 pandemic
- PMID: 34751488
- PMCID: PMC8652705
- DOI: 10.1111/irv.12932
Trends in seroprevalence of SARS-CoV-2 and infection fatality rate in the Norwegian population through the first year of the COVID-19 pandemic
Abstract
Background: Infection with the novel coronavirus SARS-CoV-2 induces antibodies that can be used as a proxy for COVID-19. We present a repeated nationwide cross-sectional study assessing the seroprevalence of SARS-CoV-2, the infection fatality rate (IFR), and infection hospitalization rate (IHR) during the first year of the pandemic in Norway.
Methods: Residual serum samples were solicited in April/May 2020 (Round 1), in July/August 2020 (Round 2) and in January 2021 (Round 3). Antibodies against SARS-CoV-2 were measured using a flow cytometer-based assay. Aggregate data on confirmed cases, COVID-19-associated deaths and hospitalizations were obtained from the Emergency preparedness registry for COVID-19 (Beredt C19), and the seroprevalence estimates were used to estimate IFR and IHR.
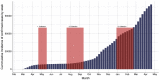
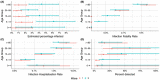
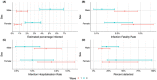
Results: Antibodies against SARS-CoV-2 were measured in 4840 samples. The estimated seroprevalence increased from 0.8% (95% credible interval [CrI] 0.4%-1.3%) after the first wave of the pandemic (Rounds 1 and 2 combined) to 3.2% (95% CrI 2.3%-4.2%) (Round 3). The IFR and IHR were higher in the first wave than in the second wave and increased with age. The IFR was 0.2% (95% CrI 0.1%-0.3%), and IHR was 0.9% (95% CrI 0.6%-1.5%) for the second wave.
Conclusions: The seroprevalence estimates show a cumulative increase of SARS-CoV-2 infections over time in the Norwegian population and suggest some under-recording of confirmed cases. The IFR and IHR were low, corresponding to the relatively low number of COVID-19-associated deaths and hospitalizations in Norway. Most of the Norwegian population was still susceptible to SARS-CoV-2 infection after the first year of the pandemic.
Keywords: COVID-19; Norway; SARS-CoV-2; infection fatality rate; infection hospitalization rate; seroprevalence.
© 2021 The Authors. Influenza and Other Respiratory Viruses published by John Wiley & Sons Ltd.
Figures

References
-
- World Health Organization (WHO) . Timeline of WHO's response to COVID‐19. 2020. https://www.who.int/news/item/29-06-2020-covidtimeline. Accessed 13.12.20.
-
- Folkehelseinstituttet . Ukerapport—uke 9. https://www.fhi.no: Folkehelseinstituttet; 10.03.21 2021.
-
- Folkehelseinstituttet . Ukerapport—uke 18. https://www.fhi.no: Folkehelseinstituttet; tirsdag 19. mai 2020 2020.
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

