NF-κB determines Paneth versus goblet cell fate decision in the small intestine
- PMID: 34751748
- PMCID: PMC8627599
- DOI: 10.1242/dev.199683
NF-κB determines Paneth versus goblet cell fate decision in the small intestine
Abstract
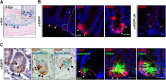
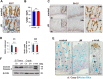
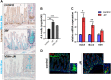
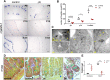
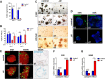
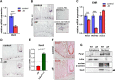
Although the role of the transcription factor NF-κB in intestinal inflammation and tumor formation has been investigated extensively, a physiological function of NF-κB in sustaining intestinal epithelial homeostasis beyond inflammation has not been demonstrated. Using NF-κB reporter mice, we detected strong NF-κB activity in Paneth cells, in '+4/+5' secretory progenitors and in scattered Lgr5+ crypt base columnar stem cells of small intestinal (SI) crypts. To examine NF-κB functions in SI epithelial self-renewal, mice or SI crypt organoids ('mini-guts') with ubiquitously suppressed NF-κB activity were used. We show that NF-κB activity is dispensable for maintaining SI epithelial proliferation, but is essential for ex vivo organoid growth. Furthermore, we demonstrate a dramatic reduction of Paneth cells in the absence of NF-κB activity, concomitant with a significant increase in goblet cells and immature intermediate cells. This indicates that NF-κB is required for proper Paneth versus goblet cell differentiation and for SI epithelial homeostasis, which occurs via regulation of Wnt signaling and Sox9 expression downstream of NF-κB. The current study thus presents evidence for an important role for NF-κB in intestinal epithelial self-renewal.
Keywords: Epithelial self-renewal; Goblet cells; Intestine; Mouse; NF-κB; Paneth cells; Stem cells.
© 2021. Published by The Company of Biologists Ltd.
Conflict of interest statement
Competing interests The authors declare no competing or financial interests.
Figures

References
-
- Bastide, P., Darido, C., Pannequin, J., Kist, R., Robine, S., Marty-Double, C., Bibeau, F., Scherer, G., Joubert, D., Hollande, F.et al. (2007). Sox9 regulates cell proliferation and is required for Paneth cell differentiation in the intestinal epithelium. J. Cell Biol. 178, 635-648. 10.1083/jcb.200704152 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials

