Polymer-Lipid Hybrid Materials
- PMID: 34752064
- PMCID: PMC11905483
- DOI: 10.1021/acs.chemrev.1c00755
Polymer-Lipid Hybrid Materials
Abstract
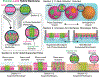
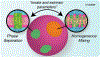
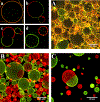
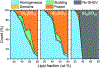
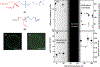
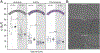
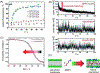
Hierarchic self-assembly underpins much of the form and function seen in synthetic or biological soft materials. Lipids are paramount examples, building themselves in nature or synthetically in a variety of meso/nanostructures. Synthetic block copolymers capture many of lipid's structural and functional properties. Lipids are typically biocompatible and high molecular weight polymers are mechanically robust and chemically versatile. The development of new materials for applications like controlled drug/gene/protein delivery, biosensors, and artificial cells often requires the combination of lipids and polymers. The emergent composite material, a "polymer-lipid hybrid membrane", displays synergistic properties not seen in pure components. Specific examples include the observation that hybrid membranes undergo lateral phase separation that can correlate in registry across multiple layers into a three-dimensional phase-separated system with enhanced permeability of encapsulated drugs. It is timely to underpin these emergent properties in several categories of hybrid systems ranging from colloidal suspensions to supported hybrid films. In this review, we discuss the form and function of a vast number of polymer-lipid hybrid systems published to date. We rationalize the results to raise new fundamental understanding of hybrid self-assembling soft materials as well as to enable the design of new supramolecular systems and applications.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing financial interest.
Figures

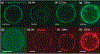
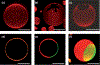
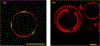
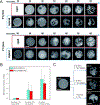

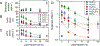
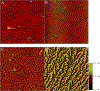
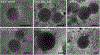
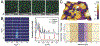
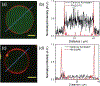
References
-
- Rideau E; Dimova R; Schwille P; Wurm FR; Landfester K Liposomes and Polymersomes: A Comparative Review Towards Cell Mimicking. Chem. Soc. Rev. 2018, 47, 8572–8610. - PubMed
-
- Le Meins JF; Schatz C; Lecommandoux S; Sandre O Hybrid Polymer/Lipid Vesicles: State of the Art and Future Perspectives. Mater. Today 2013, 16, 397–402.
-
- Schulz M; Binder WH Mixed Hybrid Lipid/Polymer Vesicles as a Novel Membrane Platform. Macromol. Rapid Commun. 2015, 36, 2031–2041. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

