Synchronized cluster firing, a distinct form of sensory neuron activation, drives spontaneous pain
- PMID: 34752775
- PMCID: PMC8776619
- DOI: 10.1016/j.neuron.2021.10.019
Synchronized cluster firing, a distinct form of sensory neuron activation, drives spontaneous pain
Abstract
Spontaneous pain refers to pain occurring without external stimuli. It is a primary complaint in chronic pain conditions and remains difficult to treat. Moreover, the mechanisms underlying spontaneous pain remain poorly understood. Here we employed in vivo imaging of dorsal root ganglion (DRG) neurons and discovered a distinct form of abnormal spontaneous activity following peripheral nerve injury: clusters of adjacent DRG neurons firing synchronously and sporadically. The level of cluster firing correlated directly with nerve injury-induced spontaneous pain behaviors. Furthermore, we demonstrated that cluster firing is triggered by activity of sympathetic nerves, which sprout into DRGs after injury, and identified norepinephrine as a key neurotransmitter mediating this unique firing. Chemogenetic and pharmacological manipulations of sympathetic activity and norepinephrine receptors suggest that they are necessary and sufficient for DRG cluster firing and spontaneous pain behavior. Therefore, blocking sympathetically mediated cluster firing may be a new paradigm for treating spontaneous pain.
Keywords: DRG; adrenergic receptors; cluster firing; dorsal root ganglion neuron; neuropathic spontaneous pain; norepinephrine; sympathetic sprouting.
Copyright © 2021 Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
Conflict of interest statement
Declaration of interests The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures
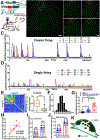

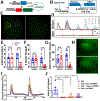
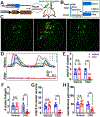

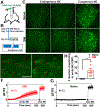
Comment in
-
Sympathetic yet painful: Autonomic innervation drives cluster firing of somatosensory neurons.Neuron. 2022 Jan 19;110(2):175-177. doi: 10.1016/j.neuron.2021.12.025. Neuron. 2022. PMID: 35051359
References
-
- Baron R (2009). Neuropathic pain: a clinical perspective. Sens. Nerves 3–30. - PubMed
-
- Bennett GJ (2012). What is spontaneous pain and who has it? J. Pain 13, 921–929. - PubMed
-
- Benzon H, Raja SN, Fishman SE, Liu SS, and Cohen SP (2011). Essentials of pain medicine E-book (Elsevier Health Sciences; ).
-
- Brumovsky P, Villar MJ, and Hökfelt T (2006). Tyrosine hydroxylase is expressed in a subpopulation of small dorsal root ganglion neurons in the adult mouse. Exp. Neurol 200, 153–165. - PubMed
-
- Charles AC, Kodali SK, and Tyndale RF (1996). Intercellular calcium waves in neurons. Mol. Cell. Neurosci 7, 337–353. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

