Placental mediated mechanisms of perinatal brain injury: Evolving inflammation and exosomes
- PMID: 34752783
- PMCID: PMC8712107
- DOI: 10.1016/j.expneurol.2021.113914
Placental mediated mechanisms of perinatal brain injury: Evolving inflammation and exosomes
Abstract
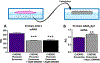
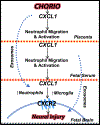
Pregnancy is an inflammatory process that is carefully regulated by the placenta via immunomodulation and cell-to-cell communication of maternal and fetal tissues. Exosomes, types of extracellular vesicles, facilitate the intercellular communication and traffic biologically modifying cargo within the maternal-placental-fetal axis in normal and pathologic pregnancies. Chorioamnionitis is characterized by inflammation of chorioamniotic membranes that produces systemic maternal and fetal inflammatory responses of cytokine dysregulation and has been associated with brain injury and neurodevelopmental disorders. This review focuses on how pathologic placental exosomes propagate acute and chronic inflammation leading to brain injury. The evidence reviewed here highlights the need to investigate exosomes from pathologic pregnancies and those with known brain injury to identify new diagnostics, biomarkers, and potential therapeutic targets.
Keywords: Chorioamnionitis; Exosomes; Inflammatory signal transduction; Perinatal brain injury.
Copyright © 2021 Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
Figures
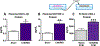
References
-
- Aires ID, Ribeiro-Rodrigues T, Boia R, et al., 2020. Exosomes derived from microglia exposed to elevated pressure amplify the neuroinflammatory response in retinal cells. Glia 68, 2705–2724. - PubMed
-
- Aisen ML, Kerkovich D, Mast J, et al., 2011. Cerebral palsy: clinical care and neurological rehabilitation. Lancet Neurol 10, 844–852. - PubMed
-
- Alvarez-Erviti L, Seow Y, Yin H, Betts C, Lakhal S, Wood MJ, 2011. Delivery of siRNA to the mouse brain by systemic injection of targeted exosomes. Nat. Biotechnol 29, 341–345. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

