EGFR High Copy Number Together With High EGFR Protein Expression Predicts Improved Outcome for Cetuximab-based Therapy in Squamous Cell Lung Cancer: Analysis From SWOG S0819, a Phase III Trial of Chemotherapy With or Without Cetuximab in Advanced NSCLC
- PMID: 34753703
- PMCID: PMC8766941
- DOI: 10.1016/j.cllc.2021.10.002
EGFR High Copy Number Together With High EGFR Protein Expression Predicts Improved Outcome for Cetuximab-based Therapy in Squamous Cell Lung Cancer: Analysis From SWOG S0819, a Phase III Trial of Chemotherapy With or Without Cetuximab in Advanced NSCLC
Abstract
Background: The phase III S0819 trial investigated addition of cetuximab to first-line chemotherapy (CT) in NSCLC. Subgroup analyses suggested an OS benefit among patients with EGFR copy number gain in squamous cell carcinomas (SCC), (HR = 0.58 [0.39-0.86], P = .0071). A more detailed model based on EGFR FISH, EGFR IHC and KRAS mutation status was evaluated to yield a more precise predictive paradigm of cetuximab-based therapy in advanced NSCLC.
Methods: FISH was performed using the Colorado Scoring Criteria; H-Score was used to quantify EGFR IHC expression (cut-off ≥ 200). A Cox model was used to assess treatment effects for OS and PFS within biomarker and clinical subgroups. KRAS mutation was analyzed using Therascreen. The false discovery rate controlled for multiple comparisons. S0819 ClinicalTrials.gov Identifier: NCT00946712.
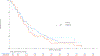
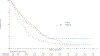
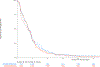
Results: Of 1,313 eligible patients, assay results were obtained for FISH on 976 patients (41% positive), for IHC on 945 patients (31% positive), and KRAS mutation status on 627 patients (26% positive). In SCC patients, OS was significantly improved with addition of cetuximab when both EGFR FISH and EGFR IHC were positive (N = 58), (OS HR: 0.32 [95% CI 0.18-0.59]; P = .0002, q = 0.08), median 12.6 versus 4.6 months. The results were independent of KRAS mutation status. In Non-SCC, no predictive value of EGFR IHC, EGFR FISH status and/or KRAS status was seen.
Conclusions: In NSCLC SCC, a combination index of EGFR FISH plus EGFR IHC results was associated with improved OS when cetuximab was added to CT, representing a potential predictive molecular paradigm for patients suitable for EGFR-antibody therapy.
Keywords: EGFR FISH; EGFR IHC; EGFR antibodies; KRAS; Survival analysis.
Copyright © 2021 Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
Conflict of interest statement
Disclosures
Fred R. Hirsch has participated in scientific advisory boards (compensated) for Bristol-Myers Squibb, Amgen, Merck, Novartis, Genentech/Roche, Sanofi, Genzyme, AstraZeneca/Daiichi, Lilly, Abbvie, and OncoCyte. Francesco Agustoni received honoraria from Roche, Bristol-Myers Squibb, Merck Sharp & Dohme, and Astra Zeneca, travel/meeting support from Incyte, and has participated in scientific advisory boards for Boehringer-Ingelheim, Merck Sharp & Dohme, and Bristol-Myers Squibb. Roy S. Herbst received research grants from AstraZeneca, Eli Lilly and Company, Genentech/Roche, and Merck and Company, compensation for consultation from Abbvie Pharmaceuticals, ARMO Biosciences, AstraZeneca, Bayer HealthCare Pharmaceuticals, Inc., Bolt Biotherapeutics, Bristol‐Myers Squibb, Candel Therapeutics, Inc., Checkpoint Therapeutics, Cybrexa Therapeutics, DynamiCure Biotechnology, LLC., eFFECTOR Therapeutics, Inc., Eli Lilly and Company, EMD Serono, Foundation Medicine, Inc., Genentech/Roche, Genmab, Gilead, Halozyme Therapeutics, Heat Biologics, HiberCell, Inc., I‐Mab Biopharma, Immune‐Onc Therapeutics, Inc., Immunocore, Infinity Pharmaceuticals, Johnson and Johnson, Loxo Oncology, Merck and Company, Mirati Therapeutics, Nektar, Neon Therapeutics, NextCure, Novartis, Ocean Biomedical, Inc., Oncocyte Corp, Oncternal Therapeutics, Pfizer, Refactor Health, Inc., Ribbon Therapeutics, Sanofi, Seattle Genetics, Shire PLC, Spectrum Pharmaceuticals, STCube Pharmaceuticals, Inc., Symphogen, Takeda, Tesaro, Tocagen, Ventana Medical Systems, Inc., WindMIL Therapeutics, and Xencor, Inc, travel/meeting support from AstraZeneca, Genentech/Roche, Merck and Company, and Ventana Medical Systems, Inc., has participated in scientific advisory boards for AstraZeneca, Bolt Biotherapeutics, Candel Therapeutics, Inc., Checkpoint Therapeutics, Cybrexa Therapeutics, EMD Serono, Halozyme Therapeutics, Heat Biologics, I‐Mab Biopharma, Immune‐Onc Therapeutics, Inc., Immunocore, Infinity Pharmaceuticals, Neon Therapeutics, Novartis, Ocean Biomedical, Inc. , Ribbon Therapeutics, STCube Pharmaceuticals, Inc., and Xencor, Inc., has served as a fiduciary role in American Association for Cancer Research, International Association for the Study of Lung Cancer, Society for Immunotherapy of Cancer, and Southwest Oncology Group, owns stock in Bolt Biotherapeutics, Checkpoint Therapeutics, and Immunocore Holdings Limited, and has been a non-executive/independent board member in Immunocore Holdings Limited and Junshi Pharmaceuticals. Karen Kelly received compensation for consultation from Eli Lilly Advisory Board. David R. Gandara received research grants from Amgen, AstraZeneca, Genentech, and Merck, compensation for consultation from Lilly, Merck, and Novartis, and has participated in scientific advisory boards for AstraZeneca, Roche-Genentech, Guardant Health, IO Biotech, and Oncocyte. Philip C. Mack has participated in scientific advisory boards and speaking engagements for Amgen and Guardant Health. Mary W. Redman, James Moon, Thomas J. Semrad, Marileila Varella-Garcia, and Chris J. Rivard declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Figures


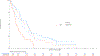
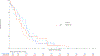
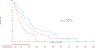
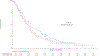
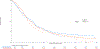
References
-
- Lynch TJ, Patel T, Dreisbach L et al. Cetuximab and first-line taxane/carboplatin chemotherapy in advanced non-small-cell lung cancer: results of the randomized multicenter phase III trial BMS099. J ClinOncol 2010; 28: 911–17. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Associated data
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

