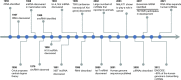
Roles and mechanisms of exosomal non-coding RNAs in human health and diseases
- PMID: 34753929
- PMCID: PMC8578673
- DOI: 10.1038/s41392-021-00779-x
Roles and mechanisms of exosomal non-coding RNAs in human health and diseases
Abstract
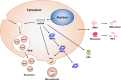
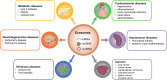
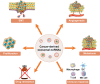
Exosomes play a role as mediators of cell-to-cell communication, thus exhibiting pleiotropic activities to homeostasis regulation. Exosomal non-coding RNAs (ncRNAs), mainly microRNAs (miRNAs), long non-coding RNAs (lncRNAs), and circular RNAs (circRNAs), are closely related to a variety of biological and functional aspects of human health. When the exosomal ncRNAs undergo tissue-specific changes due to diverse internal or external disorders, they can cause tissue dysfunction, aging, and diseases. In this review, we comprehensively discuss the underlying regulatory mechanisms of exosomes in human diseases. In addition, we explore the current knowledge on the roles of exosomal miRNAs, lncRNAs, and circRNAs in human health and diseases, including cancers, metabolic diseases, neurodegenerative diseases, cardiovascular diseases, autoimmune diseases, and infectious diseases, to determine their potential implication in biomarker identification and therapeutic exploration.
© 2021. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures

References
-
- Lakshmi S, Hughes TA, Priya S. Exosomes and exosomal RNAs in breast cancer: a status update. Eur. J. Cancer. 2021;144:252–268. - PubMed
-
- Safdar A, Saleem A, Tarnopolsky MA. The potential of endurance exercise-derived exosomes to treat metabolic diseases. Nat. Rev. Endocrinol. 2016;12:504–517. - PubMed
-
- Lin X, et al. Exosomal Notch3 from high glucose-stimulated endothelial cells regulates vascular smooth muscle cells calcification/aging. Life Sci. 2019;232:116582. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

