Clinical Impact of the Bronchiectasis with Chronic Bronchitis Symptoms in COPD: Analysis of a Longitudinal Cohort
- PMID: 34754185
- PMCID: PMC8570290
- DOI: 10.2147/COPD.S332299
Clinical Impact of the Bronchiectasis with Chronic Bronchitis Symptoms in COPD: Analysis of a Longitudinal Cohort
Abstract
Purpose: Bronchiectasis (BE) is a poor prognostic factor in COPD. However, it is not clear whether the poor prognosis is a result of BE alone or accompanying chronic bronchitis symptoms. Therefore, we investigated the effect of chronic bronchitis symptoms on clinical outcomes in COPD patients with BE.
Patients and methods: We analyzed data of COPD patients from the Korean Obstructive Lung Disease (KOLD) cohort. The presence of BE was verified by chest computed tomography. Chronic bronchitis symptoms were determined using items in the symptomatic domain of the SGRQ, which is also used as an alternative definition of chronic bronchitis (CB). Patients were divided into four groups according to the presence of BE and CB symptoms: BE/CB, BE-only, CB-only, and no BE/CB. Demographic features and clinical outcomes were compared among these groups.
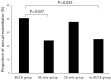
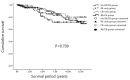
Results: In total, 389 COPD patients were included in the analysis. BE was present in 148 (38%) patients and CB symptoms were found in 123 patients (33.2%). The patients were divided according to BE and CB symptoms, and the numbers and percentages of each group were as follows: BE/CB, 52 (13.4%); BE-only, 96 (24.7%); CB-only, 77 (19.8%); no BE/CB, 164 (42.2%). No significant differences were observed in baseline characteristics of lung function, radiological findings, and inflammatory markers among the four groups. The proportion of annual exacerbators was higher in the BE/CB and CB-only groups than the other two groups. After adjusting other parameters, the BE/CB group was significantly associated with acute exacerbation of COPD (AE-COPD) (OR = 2.110, p = 0.045).
Conclusion: BE accompanying CB symptoms is associated with AE-COPD, while BE alone was not significantly associated. This finding suggests that it is more important to examine chronic bronchitis symptoms of BE to predict acute exacerbation than simply to identify BE in COPD patients.
Keywords: COPD; bronchiectasis; chronic bronchitis; exacerbation.
© 2021 Kim et al.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no conflicts of interest for this work.
Figures
References
-
- From the global strategy for the diagnosis, management and prevention of COPD, global initiative for chronic obstructive lung disease (GOLD); 2021. Available from: http://goldcopd.org. Accessed October 19, 2021.
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical