Recurrent Nephrolithiasis Due to Parathyroid Adenoma
- PMID: 34754634
- PMCID: PMC8564584
- DOI: 10.7759/cureus.18468
Recurrent Nephrolithiasis Due to Parathyroid Adenoma
Abstract
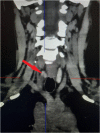
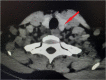
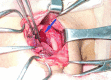
Nephrolithiasis is a common urologic disorder affecting various age groups worldwide, in association with significant morbidity. The cause associated with renal stone varies, of which increased calcium level due to primary hyperparathyroidism (parathyroid adenoma) is one of the unique and rare causes associated. The case report we are presenting is a 35-year-old female with a history of recurrent renal stones in developing country settings. Upon detailed workup, parathyroid adenoma hence was identified to be the primary culprit. She underwent parathyroidectomy and has recovered well without any complications.
Keywords: hypercalcemia; hyperparathyroidism; nephrolithiasis; parathyroid adenoma; renal stone.
Copyright © 2021, Bagale et al.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors have declared that no competing interests exist.
Figures

References
-
- Nephrolithiasis: introduction. Asplin JR. Semin Nephrol. 2008;28:97–98. - PubMed
-
- Kidney stones. Khan SR, Pearle MS, Robertson WG, et al. https://doi.org/10.1038/nrdp.2016.8. Nat Rev Dis Primers. 2016;2:16008. - PMC - PubMed
-
- Kidney stones in adults: epidemiology and risk factors. [ Aug; 2021 ];https://www.uptodate.com/contents/kidney-stones-in-adults-epidemiology-a... 2021
-
- Evaluation and management of primary hyperparathyroidism. Silverberg SJ, Bilezikian JP. https://doi.org/10.1210/jcem.81.6.8964825. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 1996;81:2036–2040. - PubMed
-
- Hyperparathyroidism in nephrolithiasis. Parks J, Coe F, Favus M. Arch Intern Med. 1980;140:1479–1481. - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
