AdipoAtlas: A reference lipidome for human white adipose tissue
- PMID: 34755127
- PMCID: PMC8561168
- DOI: 10.1016/j.xcrm.2021.100407
AdipoAtlas: A reference lipidome for human white adipose tissue
Abstract
Obesity, characterized by expansion and metabolic dysregulation of white adipose tissue (WAT), has reached pandemic proportions and acts as a primer for a wide range of metabolic disorders. Remodeling of WAT lipidome in obesity and associated comorbidities can explain disease etiology and provide valuable diagnostic and prognostic markers. To support understanding of WAT lipidome remodeling at the molecular level, we provide in-depth lipidomics profiling of human subcutaneous and visceral WAT of lean and obese individuals. We generate a human WAT reference lipidome by performing tissue-tailored preanalytical and analytical workflows, which allow accurate identification and semi-absolute quantification of 1,636 and 737 lipid molecular species, respectively. Deep lipidomic profiling allows identification of main lipid (sub)classes undergoing depot-/phenotype-specific remodeling. Previously unanticipated diversity of WAT ceramides is now uncovered. AdipoAtlas reference lipidome serves as a data-rich resource for the development of WAT-specific high-throughput methods and as a scaffold for systems medicine data integration.
Keywords: LC-MS/MS; ceramides; human white adipose tissue; lipid identification; lipid metabolism; lipidomics; obesity; plasmalogens; semi-absolute lipid quantification; sphingolipids; subcutaneous white adipose tissue; triacylglycerols; visceral white adipose tissue.
© 2021 The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
M.B. received honoraria as a consultant and speaker from Amgen, AstraZeneca, Bayer, Boehringer-Ingelheim, Lilly, Novo Nordisk, Novartis, and Sanofi. All other authors declare no competing interests.
Figures
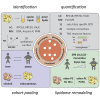

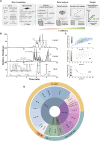

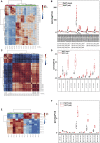

Comment in
-
AdipoAtlas: Mapping out human white adipose tissue.Cell Rep Med. 2021 Oct 19;2(10):100429. doi: 10.1016/j.xcrm.2021.100429. eCollection 2021 Oct 19. Cell Rep Med. 2021. PMID: 34755140 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Uhlén M., Fagerberg L., Hallström B.M., Lindskog C., Oksvold P., Mardinoglu A., Sivertsson Å., Kampf C., Sjöstedt E., Asplund A. Tissue-based map of the human proteome. Science. 2015;347:1260419. - PubMed
-
- Huynh K., Barlow C.K., Jayawardana K.S., Weir J.M., Mellett N.A., Cinel M., Magliano D.J., Shaw J.E., Drew B.G., Meikle P.J. High-Throughput Plasma Lipidomics: Detailed Mapping of the Associations with Cardiometabolic Risk Factors. Cell Chem. Biol. 2019;26:71–84.e4. - PubMed
-
- Seah J.Y.H., Chew W.S., Torta F., Khoo C.M., Wenk M.R., Herr D.R., Choi H., Tai E.S., van Dam R.M. Plasma sphingolipids and risk of cardiovascular diseases: a large-scale lipidomic analysis. Metabolomics. 2020;16:89. - PubMed
-
- Frayn K.N., Arner P., Yki-Järvinen H. Fatty acid metabolism in adipose tissue, muscle and liver in health and disease. Essays Biochem. 2006;42:89–103. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

