Adalimumab and sulfasalazine in alleviating sacroiliac and aortic inflammation detected in PET/CT in patients with axial spondyloarthritis: PETSPA
- PMID: 34755937
- PMCID: PMC8767522
- DOI: 10.1002/iid3.552
Adalimumab and sulfasalazine in alleviating sacroiliac and aortic inflammation detected in PET/CT in patients with axial spondyloarthritis: PETSPA
Abstract
Aim: Inflammatory signals in the sacroiliac (SI) joints and the aorta of patients with axial spondyloarthritis (axSpA) were graded by positron emission tomography/computed tomography (PET/CT) imaging before and after treatment with sulfasalazine (SSZ) or adalimumab (ADA).
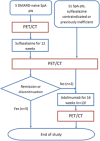
Methods: Patients with axSpA, Bath Ankylosing Spondylitis Disease Activity Index (BASDAI) ≥ 4, were recruited. Disease-modifying antirheumatic drug-naïve patients started SSZ for 12 weeks, whereas those with prestudy treatment with or contraindication to SSZ commenced ADA for 16 weeks. In addition, those patients in the SSZ group with insufficient response commenced ADA for 16 weeks. 18F-fluorodeoxyglucose PET/CT was performed after inclusion and after treatment with SSZ and ADA. Maximum standardized uptake value (SUVmax) was assessed for the aorta and the SI joints, and maximal target-to-blood-pool ratio (TBRmax) only for the aorta.
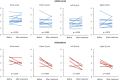
Results: Among five SSZ patients, mean ± SD BASDAI was 4.7 ± 1.6 before and 3.5 ± 1.4 after treatment (p = .101). In 13 ADA patients, the BASDAI decreased from 5.4 ± 1.6 to 2.8 ± 2.2 (p < .001). Among the SSZ patients, SUVmax in SI joints decreased from 2.35 ± 0.55 to 1.51 ± 0.22 (-35.8%, p = .029). Aortic TBRmax decreased from 1.59 ± 0.43 to 1.26 ± 0.26 (-33.2%, p = .087). In the ADA patients, SUVmax in the SI joints was 1.92 ± 0.65 before and 1.88 ± 0.54 after treatment (-1.8%, p = .808) and TBRmax in the aorta 1.50 ± 0.60 before and 1.40 ± 0.26 after treatment (-6.7%, p = .485).
Conclusions: Our small open-label study showed that SSZ may reduce PET-CT-detectable inflammation in the SI joints, with a trend towards a reduction in the aorta.
Keywords: adalimumab; axial spondyloarthritis; inflammation; positron emission tomography/computed tomography; sulfasalazine.
© 2021 The Authors. Immunity, Inflammation and Disease published by John Wiley & Sons Ltd.
Conflict of interest statement
Anne M. Kerola has received speaker fees from Boehringer‐Ingelheim and Sanofi, has attended advisory boards of Pfizer, Gilead, and Boehringer‐Ingelheim, and received congress sponsorship from Pfizer, Celgene, UCB Pharma, Mylan, and Roche. Riitta Tuompo has received speaker fees from Mylan, and congress sponsorship from Roche and Novartis. Other authors declare that there are no conflict of interests.
Figures
References
-
- Rudwaleit M, Landewé R, van der Heijde D, et al. The development of Assessment of SpondyloArthritis International Society classification criteria for axial spondyloarthritis (part I): classification of paper patients by expert opinion including uncertainty appraisal. Ann Rheum Dis. 2009;68:770‐776. 10.1136/ard.2009.108217 - DOI - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials

