Selective targeting of NaV1.7 via inhibition of the CRMP2-Ubc9 interaction reduces pain in rodents
- PMID: 34757807
- PMCID: PMC11729770
- DOI: 10.1126/scitranslmed.abh1314
Selective targeting of NaV1.7 via inhibition of the CRMP2-Ubc9 interaction reduces pain in rodents
Abstract
The voltage-gated sodium NaV1.7 channel, critical for sensing pain, has been actively targeted by drug developers; however, there are currently no effective and safe therapies targeting NaV1.7. Here, we tested whether a different approach, indirect NaV1.7 regulation, could have antinociceptive effects in preclinical models. We found that preventing addition of small ubiquitin-like modifier (SUMO) on the NaV1.7-interacting cytosolic collapsin response mediator protein 2 (CRMP2) blocked NaV1.7 functions and had antinociceptive effects in rodents. In silico targeting of the SUMOylation site in CRMP2 (Lys374) identified >200 hits, of which compound 194 exhibited selective in vitro and ex vivo NaV1.7 engagement. Orally administered 194 was not only antinociceptive in preclinical models of acute and chronic pain but also demonstrated synergy alongside other analgesics—without eliciting addiction, rewarding properties, or neurotoxicity. Analgesia conferred by 194 was opioid receptor dependent. Our results demonstrate that 194 is a first-in-class protein-protein inhibitor that capitalizes on CRMP2-NaV1.7 regulation to deliver safe analgesia in rodents.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures

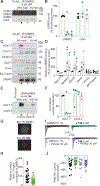
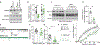

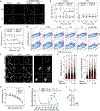

Comment in
-
Navigating a new path to Nav1.7 for pain.Nat Rev Drug Discov. 2022 Jan;21(1):18. doi: 10.1038/d41573-021-00197-2. Nat Rev Drug Discov. 2022. PMID: 34824392 No abstract available.
References
-
- Meents JE, Bressan E, Sontag S, Foerster A, Hautvast P, Rösseler C, Hampl M, Schüler H, Goetzke R, Le TKC, Kleggetveit IP, Cann KL, Kerth C, Rush AM, Rogers M, Kohl Z, Schmelz M, Wagner W, Jørum E, Namer B, Winner B, Zenke M, Lampert A, The role of Nav1.7 in human nociceptors: Insights from human induced pluripotent stem cell-derived sensory neurons of erythromelalgia patients. Pain 160, 1327–1341 (2019). - PMC - PubMed
-
- Waxman SG, Zamponi GW, Regulating excitability of peripheral afferents: Emerging ion channel targets. Nat. Neurosci. 17, 153–163 (2014). - PubMed
-
- Dib-Hajj SD, Yang Y, Black JA, Waxman SG, The Na(V)1.7 sodium channel: From molecule to man. Nat. Rev. Neurosci. 14, 49–62 (2013). - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous

