Oral Vaccination Protects Against Severe Acute Respiratory Syndrome Coronavirus 2 in a Syrian Hamster Challenge Model
- PMID: 34758086
- PMCID: PMC8689930
- DOI: 10.1093/infdis/jiab561
Oral Vaccination Protects Against Severe Acute Respiratory Syndrome Coronavirus 2 in a Syrian Hamster Challenge Model
Abstract
Background: Vaccines that are shelf stable and easy to administer are crucial to improve vaccine access and reduce severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2 (SARS-CoV-2) transmission around the world.
Methods: In this study, we demonstrate that an oral, adenovirus-based vaccine candidate protects against SARS-CoV-2 in a Syrian hamster challenge model.
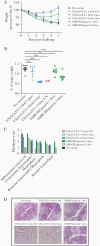
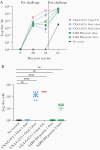
Results: Hamsters administered 2 doses of VXA-CoV2-1 showed a reduction in weight loss and lung pathology and had completely eliminated infectious virus 5 days postchallenge. Oral immunization induced antispike immunoglobulin G, and neutralizing antibodies were induced upon oral immunization with the sera, demonstrating neutralizing activity.
Conclusions: Overall, these data demonstrate the ability of oral vaccine candidate VXA-CoV2-1 to provide protection against SARS-CoV-2 disease.
Keywords: COVID; SARS-CoV-2; hamster; mucosal; oral vaccine.
© The Author(s) 2021. Published by Oxford University Press for the Infectious Diseases Society of America. All rights reserved. For permissions, e-mail: journals.permissions@oup.com.
Figures

References
-
- Wang P, Nair MS, Liu L, et al. Antibody resistance of SARS-CoV-2 variants B.1.351 and B.1.1.7. Nature 2021; 593:130–5. - PubMed
-
- Farstad IN, Halstensen TS, Lazarovits AI, Norstein J, Fausa O, Brandtzaeg P. Human intestinal B-cell blasts and plasma cells express the mucosal homing receptor integrin alpha 4 beta 7. Scand J Immunol 1995; 42:662–72. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

