E2F transcription factor 1 elevates cyclin D1 expression by suppressing transcription of microRNA-107 to augment progression of glioma
- PMID: 34758200
- PMCID: PMC8671784
- DOI: 10.1002/brb3.2399
E2F transcription factor 1 elevates cyclin D1 expression by suppressing transcription of microRNA-107 to augment progression of glioma
Abstract
Background: Dysregulation of microRNAs has been frequently implicated in the progression of human diseases, including glioma. This study aims to explore the interaction between E2F transcription factor 1 (E2F1) and miR-107 in the progression of glioma.
Methods: Expression of miR-107 in glioma tissues and cells was examined. Putative binding sites between E2F1 and the promoter region of miR-107, and between miR-107 and cyclin D1 (CCND1) mRNA were predicted via bioinformatic systems and validated via chromatin immunoprecipitation and luciferase reporter gene assays. Altered expression of miR-107, E2F1, and CCND1 was introduced in A172 and T98G cells to examine their roles in cell growth and the activity of the Wnt/β-catenin signaling. In vivo experiments were performed by injecting cells in nude mice.
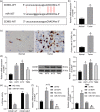
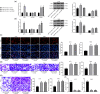
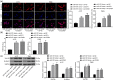
Results: miR-107 was poorly expressed, whereas E2F1 and CCND1 were highly expressed in glioma tissues and cells. E2F1 bound to the promoter region of miR-107 to induce transcriptional repression, and miR-107 directly bound to CCND1 mRNA to reduce its expression. Overexpression of miR-107 reduced proliferation, migration and invasion, and augmented apoptosis of glioma cells, and it reduced activity of the Wnt/β-catenin pathway. The anti-tumorigenic roles of miR-107 were blocked by E2F1 or CCND1 overexpression. Similar results were reproduced in vivo where miR-107 overexpression or E2F1 inhibition blocked tumor growth in nude mice.
Conclusion: This study suggested that E2F1 reduces miR-107 transcription to induce CCND1 upregulation, which leads to progression of glioma via Wnt/β-catenin signaling activation.
Keywords: E2F transcription factor 1; Wnt/β-catenin; cyclin D1; glioma; miR-107.
© 2021 The Authors. Brain and Behavior published by Wiley Periodicals LLC.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures




References
-
- Aguilar, C. , Costa, S. , Maudet, C. , Vivek‐Ananth, R. P. , Zaldivar‐Lopez, S. , Garrido, J. J. , Samal, A. Mano, M. , & Eulalio, A. (2021). Reprogramming of microRNA expression via E2F1 downregulation promotes Salmonella infection both in infected and bystander cells. Nature Communications, 12(1), 3392. 10.1038/s41467-021-23593-z - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Alqudah, M. A. , Agarwal, S. , Al‐Keilani, M. S. , Sibenaller, Z. A. , Ryken, T. C. , & Assem, M. (2013). NOTCH3 is a prognostic factor that promotes glioma cell proliferation, migration, and invasion via activation of CCND1 and EGFR. PLOS One, 8(10), e77299. 10.1371/journal.pone.0077299 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials

