The organization and development of cortical interneuron presynaptic circuits are area specific
- PMID: 34758329
- PMCID: PMC8832360
- DOI: 10.1016/j.celrep.2021.109993
The organization and development of cortical interneuron presynaptic circuits are area specific
Abstract
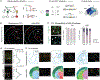
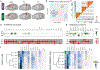
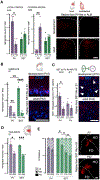
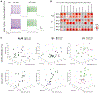
Parvalbumin and somatostatin inhibitory interneurons gate information flow in discrete cortical areas that compute sensory and cognitive functions. Despite the considerable differences between areas, individual interneuron subtypes are genetically invariant and are thought to form canonical circuits regardless of which area they are embedded in. Here, we investigate whether this is achieved through selective and systematic variations in their afferent connectivity during development. To this end, we examined the development of their inputs within distinct cortical areas. We find that interneuron afferents show little evidence of being globally stereotyped. Rather, each subtype displays characteristic regional connectivity and distinct developmental dynamics by which this connectivity is achieved. Moreover, afferents dynamically regulated during development are disrupted by early sensory deprivation and in a model of fragile X syndrome. These data provide a comprehensive map of interneuron afferents across cortical areas and reveal the logic by which these circuits are established during development.
Keywords: ALM; GABAergic interneurons; cortical areas; development; fragile X syndrome; monosynaptic rabies tracing; sensory cortex; thalamocortical input.
Copyright © 2021 The Author(s). Published by Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
Conflict of interest statement
Declaration of interests Gord Fishell is a founder of Regel Therapeutics, which has no competing interests with the present manuscript.
Figures

References
-
- Ährlund-Richter S, Xuan Y, van Lunteren JA, Kim H, Ortiz C, Pollak Dorocic I, Meletis K, and Carlén M (2019). A whole-brain atlas of monosynaptic input targeting four different cell types in the medial prefrontal cortex of the mouse. Nat. Neurosci 22, 657–668. 10.1038/s41593-019-0354-y. - DOI - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials

