Circulating Plasma Biomarkers in Biopsy-Confirmed Kidney Disease
- PMID: 34759008
- PMCID: PMC8763150
- DOI: 10.2215/CJN.09380721
Circulating Plasma Biomarkers in Biopsy-Confirmed Kidney Disease
Abstract
Background and objectives: Biomarkers for noninvasive assessment of histopathology and prognosis are needed in patients with kidney disease.
Design, setting, participants, & measurements: Using a proteomics assay, we measured a multimarker panel of 225 circulating plasma proteins in a prospective cohort study of 549 individuals with biopsy-confirmed kidney diseases and semiquantitative assessment of histopathology. We tested the associations of each biomarker with histopathologic lesions and the risks of kidney disease progression (defined as ≥40% decline in eGFR or initiation of KRT) and death.
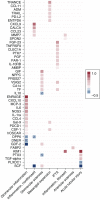
Results: After multivariable adjustment and correction for multiple testing, 46 different proteins were associated with histopathologic lesions. The top-performing markers positively associated with acute tubular injury and interstitial fibrosis/tubular atrophy were kidney injury molecule-1 (KIM-1) and V-set and Ig domain-containing protein 2 (VSIG2), respectively. Thirty proteins were significantly associated with kidney disease progression, and 35 were significantly associated with death. The top-performing markers for kidney disease progression were placental growth factor (hazard ratio per doubling, 5.4; 95% confidence interval, 3.4 to 8.7) and BMP and activin membrane-bound inhibitor (hazard ratio, 3.0; 95% confidence interval, 2.1 to 4.2); the top-performing markers for death were TNF-related apoptosis-inducing ligand receptor-2 (hazard ratio, 2.9; 95% confidence interval, 2.0 to 4.0) and CUB domain-containing protein-1 (hazard ratio, 2.4; 95% confidence interval, 1.8 to 3.3).
Conclusion: We identified several plasma protein biomarkers associated with kidney disease histopathology and adverse clinical outcomes in individuals with a diverse set of kidney diseases.
Podcast: This article contains a podcast at https://www.asn-online.org/media/podcast/CJASN/2021_12_28_CJN09380721.mp3.
Keywords: Boston; biomarkers; causality; cohort studies; histopathology; kidney biopsy; kidney disease; nephrectomy; plasma; proteomics.
Copyright © 2022 by the American Society of Nephrology.
Figures


References
-
- Sabbisetti VS, Waikar SS, Antoine DJ, Smiles A, Wang C, Ravisankar A, Ito K, Sharma S, Ramadesikan S, Lee M, Briskin R, De Jager PL, Ngo TT, Radlinski M, Dear JW, Park KB, Betensky R, Krolewski AS, Bonventre JV: Blood kidney injury molecule-1 is a biomarker of acute and chronic kidney injury and predicts progression to ESRD in type I diabetes. J Am Soc Nephrol 25: 2177–2186, 2014 - PMC - PubMed
-
- Waikar SS, Sabbisetti V, Ärnlöv J, Carlsson AC, Coresh J, Feldman HI, Foster MC, Fufaa GD, Helmersson-Karlqvist J, Hsu CY, Kimmel PL, Larsson A, Liu Y, Lind L, Liu KD, Mifflin TE, Nelson RG, Risérus U, Vasan RS, Xie D, Zhang X, Bonventre JV; Chronic Kidney Disease Biomarkers Consortium Investigators : Relationship of proximal tubular injury to chronic kidney disease as assessed by urinary kidney injury molecule-1 in five cohort studies. Nephrol Dial Transplant 31: 1460–1470, 2016 - PMC - PubMed
-
- Niewczas MA, Pavkov ME, Skupien J, Smiles A, Md Dom ZI, Wilson JM, Park J, Nair V, Schlafly A, Saulnier PJ, Satake E, Simeone CA, Shah H, Qiu C, Looker HC, Fiorina P, Ware CF, Sun JK, Doria A, Kretzler M, Susztak K, Duffin KL, Nelson RG, Krolewski AS: A signature of circulating inflammatory proteins and development of end-stage renal disease in diabetes. Nat Med 25: 805–813, 2019 - PMC - PubMed
-
- Ganz P, Heidecker B, Hveem K, Jonasson C, Kato S, Segal MR, Sterling DG, Williams SA: Development and validation of a protein-based risk score for cardiovascular outcomes among patients with stable coronary heart disease. JAMA 315: 2532–2541, 2016 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
- K08 DK126847/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- R01 DK093574/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- R01 DK103784/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- U2C DK114886/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- UL1 TR001102/TR/NCATS NIH HHS/United States
- T32 DK007199/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- U01 DK104308/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- UH3 DK114915/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- K23 DK120811/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- P30 DK114857/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- U01 DK085660/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- R21 DK119751/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

