Moderate-intensity exercise alleviates pyroptosis by promoting autophagy in osteoarthritis via the P2X7/AMPK/mTOR axis
- PMID: 34759265
- PMCID: PMC8580998
- DOI: 10.1038/s41420-021-00746-z
Moderate-intensity exercise alleviates pyroptosis by promoting autophagy in osteoarthritis via the P2X7/AMPK/mTOR axis
Abstract
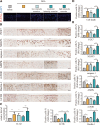
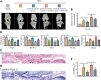
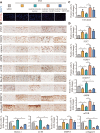
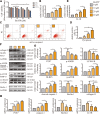
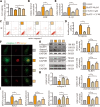
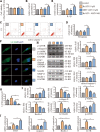
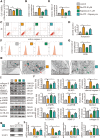
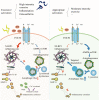
Instability and excessive use of the knee joint can cause osteoarthritis (OA). Reasonable exercise can enhance the stability of the knee joint and prevent and relieve the occurrence and development of OA. As a key switch for inflammation, P2X purinoceptor 7 (P2X7) has attracted much attention in studies of OA. Exercise can regulate P2X7 expression and activation. However, the role of P2X7 in exercise-based prevention and treatment of OA is unknown. We previously showed that moderate-intensity exercise can significantly alleviate OA symptoms. Accordingly, in this study, we evaluated the effects of exercise on P2X7 expression and activation in chondrocytes. Micro-computed tomography, hematoxylin, and eosin staining, Toluidine Blue O staining, immunohistochemistry, and terminal deoxynucleotidyl transferase dUTP nick-end labeling experiments showed that P2X7 expression was lower in the moderate-intensity exercise group than in the inflammation and low- and high-intensity exercise groups. Additionally, chondrocyte death, cartilage destruction, and the degree and severity of pyroptosis were significantly reduced, whereas autophagy levels were significantly increased in the moderate-intensity exercise group. Cell Counting Kit-8 assay, lactate dehydrogenase release, flow cytometry, enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay, cell fluorescence, western blot, reverse transcription-quantitative polymerase chain reaction, and transmission electron microscopy experiments showed that moderate activation of P2X7 promoted autophagy through the AMP-activated protein kinase (AMPK)/mammalian target of rapamycin (mTOR) signaling pathway and promoted autolysosome targeting for degradation of the inflammasome component NLRP3, thereby inhibiting pyroptosis. Additionally, the use of AMPK and mTOR activators and inhibitors indicated that the AMPK-mTOR signaling pathway, as the downstream of P2X7, played a key role in delaying the occurrence and development of OA. We propose that moderate-intensity exercise promoted chondrocyte autophagy through the P2X7/AMPK/mTOR signal axis to alleviate pyroptosis. Our findings provide novel insights into the positive and preventative effects of exercise on OA.
© 2021. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures
Similar articles
-
IRE1-mTOR-PERK Axis Coordinates Autophagy and ER Stress-Apoptosis Induced by P2X7-Mediated Ca2+ Influx in Osteoarthritis.Front Cell Dev Biol. 2021 Jun 17;9:695041. doi: 10.3389/fcell.2021.695041. eCollection 2021. Front Cell Dev Biol. 2021. PMID: 34222263 Free PMC article.
-
P2X7 Receptor Induces Pyroptotic Inflammation and Cartilage Degradation in Osteoarthritis via NF-κB/NLRP3 Crosstalk.Oxid Med Cell Longev. 2021 Jan 16;2021:8868361. doi: 10.1155/2021/8868361. eCollection 2021. Oxid Med Cell Longev. 2021. PMID: 33532039 Free PMC article.
-
Linear ubiquitination of LKB1 activates AMPK pathway to inhibit NLRP3 inflammasome response and reduce chondrocyte pyroptosis in osteoarthritis.J Orthop Translat. 2022 Dec 1;39:1-11. doi: 10.1016/j.jot.2022.11.002. eCollection 2023 Mar. J Orthop Translat. 2022. PMID: 36514784 Free PMC article.
-
The P2X7 Receptor in Osteoarthritis.Front Cell Dev Biol. 2021 Feb 11;9:628330. doi: 10.3389/fcell.2021.628330. eCollection 2021. Front Cell Dev Biol. 2021. PMID: 33644066 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Effect of moderate exercise on osteoarthritis.EFORT Open Rev. 2023 Mar 14;8(3):148-161. doi: 10.1530/EOR-22-0119. EFORT Open Rev. 2023. PMID: 36916731 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Endurance exercise preconditioning alleviates ferroptosis induced by doxorubicin-induced cardiotoxicity through mitochondrial superoxide-dependent AMPKα2 activation.Redox Biol. 2024 Apr;70:103079. doi: 10.1016/j.redox.2024.103079. Epub 2024 Feb 8. Redox Biol. 2024. PMID: 38359747 Free PMC article.
-
SNORC knockdown alleviates inflammation, autophagy defect and matrix degradation of chondrocytes in osteoarthritis development.Mol Cell Biochem. 2024 Sep;479(9):2323-2335. doi: 10.1007/s11010-023-04842-9. Epub 2023 Sep 2. Mol Cell Biochem. 2024. PMID: 37659033
-
Targeting inflammasome-dependent mechanisms as an emerging pharmacological approach for osteoarthritis therapy.iScience. 2022 Nov 11;25(12):105548. doi: 10.1016/j.isci.2022.105548. eCollection 2022 Dec 22. iScience. 2022. PMID: 36465135 Free PMC article. Review.
-
MiR-29a-3p mediates phosphatase and tensin homolog and inhibits osteoarthritis progression.Funct Integr Genomics. 2024 Mar 12;24(2):54. doi: 10.1007/s10142-024-01327-w. Funct Integr Genomics. 2024. PMID: 38467932
-
Autophagy in the pathogenesis and therapeutic potential of post-traumatic osteoarthritis.Burns Trauma. 2023 Jan 31;11:tkac060. doi: 10.1093/burnst/tkac060. eCollection 2023. Burns Trauma. 2023. PMID: 36733467 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Carr AJ, Robertsson O, Graves S, Price AJ, Arden NK, Judge A, et al. Knee replacement. Lancet. 2012;379:1331–40. - PubMed
-
- Surprenant A, Rassendren F, Kawashima E, North RA, Buell G. The cytolytic P2Z receptor for extracellular ATP identified as a P2X receptor (P2X7) Science. 1996;272:735–38. - PubMed
-
- North RA. Molecular physiology of P2X receptors. Physiol Rev. 2002;82:1013–67. - PubMed
-
- Pétrilli V, Papin S, Dostert C, Mayor A, Martinon F, Tschopp J. Activation of the NALP3 inflammasome is triggered by low intracellular potassium concentration. Cell Death Differ. 2007;14:1583–9. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

