A Systematic Review on the Therapeutic Relevance of Hydroxychloroquine/Chloroquine in the Management of COVID-19
- PMID: 34759472
- PMCID: PMC8575213
- DOI: 10.4103/ijcm.IJCM_539_20
A Systematic Review on the Therapeutic Relevance of Hydroxychloroquine/Chloroquine in the Management of COVID-19
Abstract
Background: The coronavirus disease-2019 (COVID-19) pandemic is coming to the fore and has surfaced as a public health emergency of international concern. The lack of vaccines or an effective treatment has led to the global hunt for potential pharmaceuticals in adequately managing this disease. This systematic review highlights the efficacy of chloroquine and its derivative hydroxychloroquine in the treatment of COVID-19 and also explores the safety profile of these drugs.
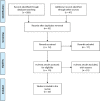
Methods: EMBASE, COCHRANE, and PubMed databases were searched for studies on the use of hydroxychloroquine or chloroquine in the treatment of COVID-19.
Results: Twenty articles were selected including expert opinions, National Guidelines, three small randomized controlled trials, and one prospective study. Both hydroxychloroquine and chloroquine have shown promising results including reduction in hospital length of stay and overall mortality. Moreover, concomitant use with azithromycin seems to reduce viral load to a greater extent.
Conclusions: Considering the known safety profile of these drugs in the treatment of other diseases, their availability and affordability, chloroquine and hydroxychloroquine are potential antiviral agents in the treatment of COVID-19. However, reported side effects of these drugs when used in conjunction with azithromycin in patients with comorbidities have raised significant safety concerns. High-quality randomized clinical trials are warranted to provide more comprehensive evidence of the safety of these drugs in patients infected with COVID-19.
Keywords: Chloroquine; coronavirus; coronavirus disease 2019; hydroxychloroquine; pneumonia; severe acute respiratory syndrome-CoV-2.
Copyright: © 2021 Indian Journal of Community Medicine.
Conflict of interest statement
There are no conflicts of interest.
Figures
References
-
- [Last accessed on 2020 Aug 17]. Available from: https://www.worldometers.info/coronavirus/
-
- [Last accessed on 2020 Sep 01]. Available from: https://www.who.int/news-room/commentaries/detail/transmission-of-sars-c... .
-
- Liu Q, Wang R, Qu G, Wang Y, Liu P, Zhu Y. General anatomy report of novel coronavirus pneumonia patients. J Forensic Med. 2020;36:21–23.
-
- Gao J, Tian Z, Yang X. Breakthrough: Chloroquine phosphate has shown apparent efficacy in treatment of COVID-19 associated pneumonia in clinical studies. Biosci Trends. 2020;14:72–3. - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources