Allosteric inhibition of SARS-CoV-2 3CL protease by colloidal bismuth subcitrate
- PMID: 34760193
- PMCID: PMC8565384
- DOI: 10.1039/d1sc03526f
Allosteric inhibition of SARS-CoV-2 3CL protease by colloidal bismuth subcitrate
Abstract
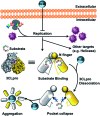
The SARS-CoV-2 3-chymotrypsin-like protease (3CLpro or Mpro) is a key cysteine protease for viral replication and transcription, making it an attractive target for antiviral therapies to combat the COVID-19 disease. Here, we demonstrate that bismuth drug colloidal bismuth subcitrate (CBS) is a potent inhibitor for 3CLpro in vitro and in cellulo. Rather than targeting the cysteine residue at the catalytic site, CBS binds to an allosteric site and results in dissociation of the 3CLpro dimer and proteolytic dysfunction. Our work provides direct evidence that CBS is an allosteric inhibitor of SARS-CoV-2 3CLpro.
This journal is © The Royal Society of Chemistry.
Conflict of interest statement
There are no conflicts to declare.
Figures




References
-
- Zhou P. Yang X.-L. Wang X.-G. Hu B. Zhang L. Zhang W. Si H.-R. Zhu Y. Li B. Huang C.-L. Chen H.-D. Chen J. Luo Y. Guo H. Jiang R.-D. Liu M.-Q. Chen Y. Shen X.-R. Wang X. Zheng X.-S. Zhao K. Chen Q.-J. Deng F. Liu L.-L. Yan B. Zhan F.-X. Wang Y.-Y. Xiao G.-F. Shi Z.-L. Nature. 2020;588(7836):E6. doi: 10.1038/s41586-020-2951-z. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Jin Z. Du X. Xu Y. Deng Y. Liu M. Zhao Y. Zhang B. Li X. Zhang L. Peng C. Duan Y. Yu J. Wang L. Yang K. Liu F. Jiang R. Yang X. You T. Liu X. Yang X. Bai F. Liu H. Liu X. Guddat L. W. Xu W. Xiao G. Qin C. Shi Z. Jiang H. Rao Z. Yang H. Nature. 2020;582(7811):289–293. doi: 10.1038/s41586-020-2223-y. - DOI - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous

